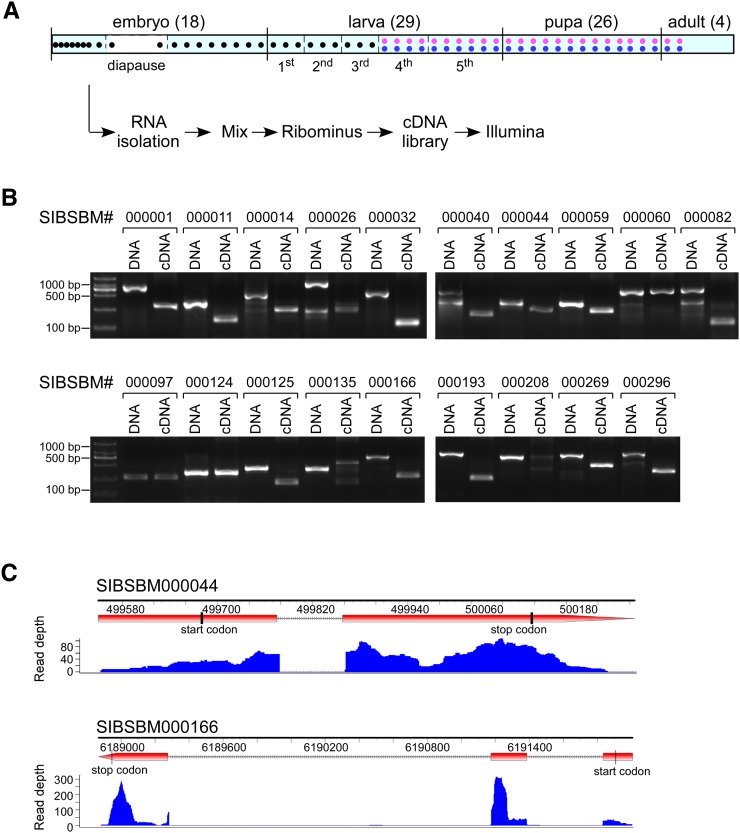
FIGURE 1.
RNA-seq and the identification of novel genes in B. mori. (A) Strategy for RNA-seq in the silkworm. Total RNAs were isolated from samples at different stages throughout the lifetime of the silkworm as indicated and mixed together in equal parts. After depletion of ribosomal RNAs, reverse transcription, and fragmentation, double-stranded cDNAs were sequenced on an Illumina Genome Analyzer. (B) Validation of the predicted novel genes by RT-PCR. Twenty novel genes were randomly selected and amplified from genomic DNA and cDNA templates. Migration differences between two templates indicate that the gene contains one or more introns. Validation failure could be caused by inaccurate genome information or poor PCR amplification. (C) Distribution of the RNA-seq reads that support exon and intron boundaries for novel genes. The positions of the start and stop codons and the depth of supported reads are indicated. RT-PCR analysis, shown in panel B, confirmed that these two novel genes contained intron(s).