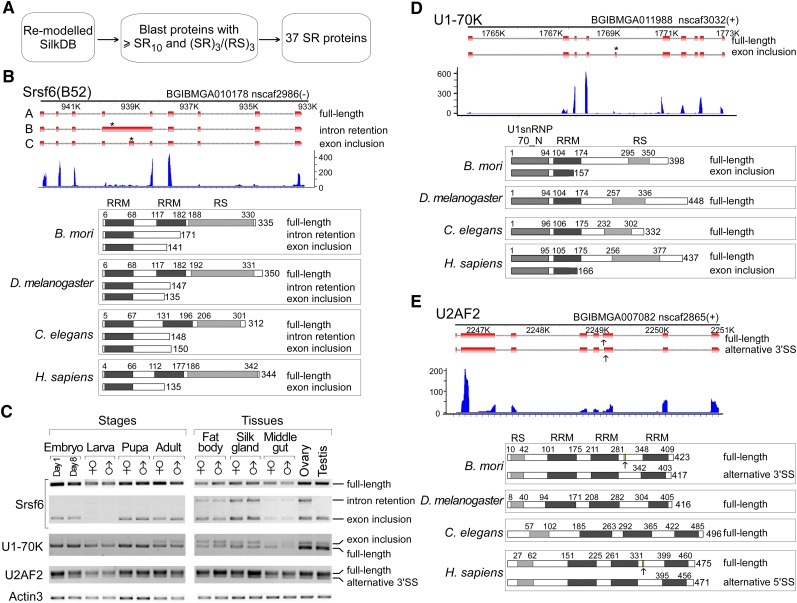
FIGURE 3.
Alternative splicing of three SR proteins are conserved from silkworm to human. (A) Strategy for searching for SR proteins from the silkworm. (B) Alternative splicing of Srsf6 is highly conserved across species from silkworms to humans. Three alternatively spliced isoforms of Bm Srsf6 were identified by RNA-seq analysis. Early stop codons in the intron-retention and exon-inclusion isoforms of Srsf6 are indicated by asterisks (upper). Both alternative splicing types and the resulting SRSF6 protein isoforms are conserved in the silkworm, D. melanogaster, C. elegans, and humans (bottom). (C) mRNA profiles of Srsf6, U1-70K, and U2AF2 in different developmental stages and tissues. Each isoform amplified by RT-PCR was isolated and confirmed by sequencing. Actin3 was used as a loading control. Alternatively spliced isoforms of (D) U1-70K and (E) U2AF2 are conserved in the silkworm and human. The absence of related isoforms in D. melanogaster and C. elegans might be due to incomplete investigation. All of the mRNA sequences from D. melanogaster, C. elegans, and human were retrieved from the NCBI database. The SR domain and RNA recognition motif (RRM) in SRSF6 are indicated.