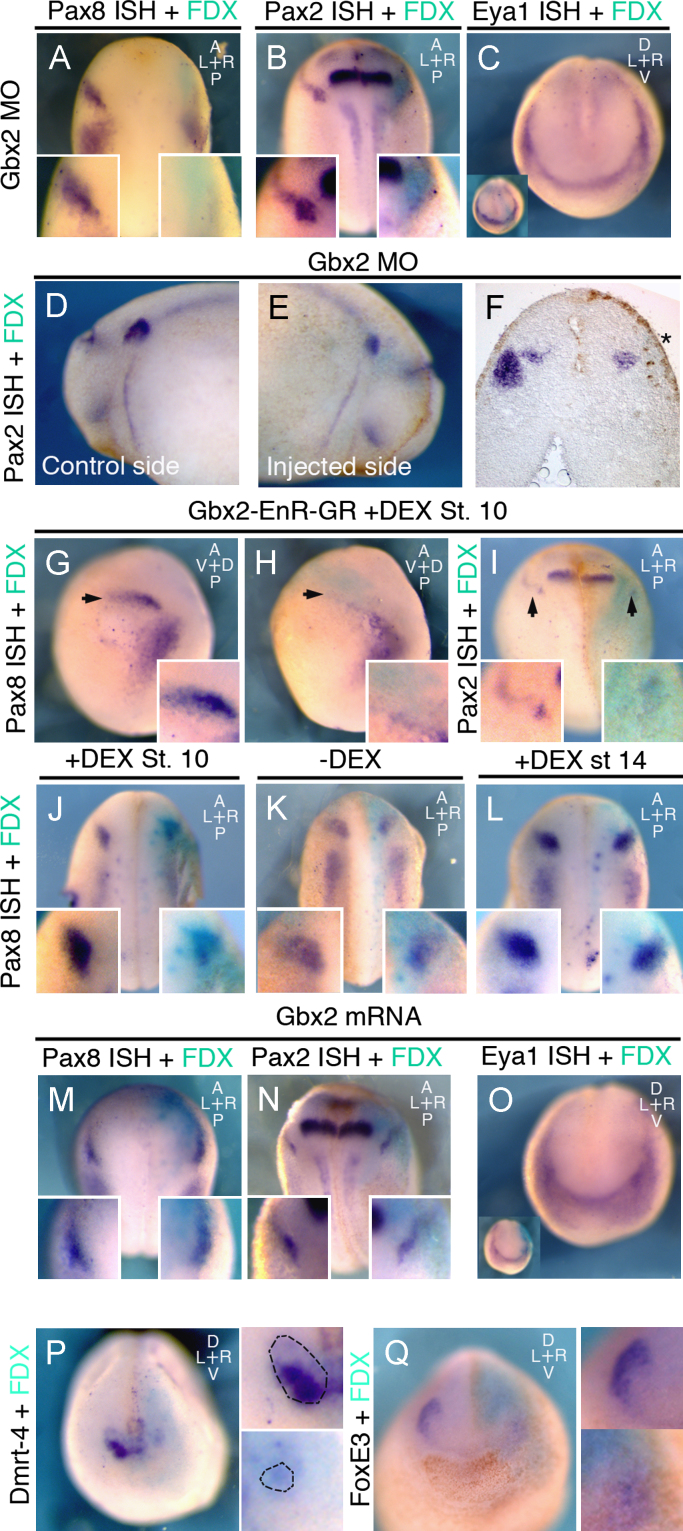
Fig. 4.
Gbx2 is required for otic specification. (A)–(C) Injection of splice and translation blocking Gbx2 morpholinos inhibits otic Pax8 (A; 54%, n=28) and otic Pax2 ((B); 55%, n=131; Splice MO: 66% affected, n=29; ATG MO: 49% affected, n=79). There is no effect on Eya1 (0% affected, n=30. (C): blue). (D)–(F) At stage 25, Pax2 expression is reduced and the otic vesicle is small (asterisk in transverse section F) after injection of splice and translation blocking Gbx2 morpholinos ((E) 59% affected, n=66; splice MO: 44% affected, n=25) when compared to the uninjected side (D). (G)–(I) Injection of inducible Gbx2-EnR-GR: activation at stage 10 reduces otic Pax8 (arrow) at stage 13 ((H); 49%, n=43) compared to uninjected side (G) and Pax2 at stage 16 ((I); arrow; 46% n=18). (J)–(L) Activation of inducible Gbx2-EnR-GR at stage 10 (J) reduces Pax8; no change is observed in absence of DEX ((K); 0% affected, n=17) or when DEX is added at stage 14 ((L) 0% affected, n=110). (M)–(O) Gbx2 mRNA does not expand Pax8 ((M); 0% affected, n=35), Pax2 ((N); 0% affected, n=22), and Eya1 ((O) 0% affected, n=22). (P), (Q) Overexpression of Gbx2 reduces Dmrt-4 ((P) 66%, n=29) and FoxE3 ((Q) 92%, n=13). Small panels in (P) and (Q) show higher magnification of the control (top) and injected (bottom) side. All embryos were injected into the A3 blastomere at the 32-cell stage; inserts in (A), (B), (G)–(N) high magnification of the otic region. In (C) and (O) turquoise staining reveals FDX. Crosses indicate the orientation of embryos; a: anterior, l: left, p: posterior, r: right, d: dorsal, v: ventral.