Fig. 2.
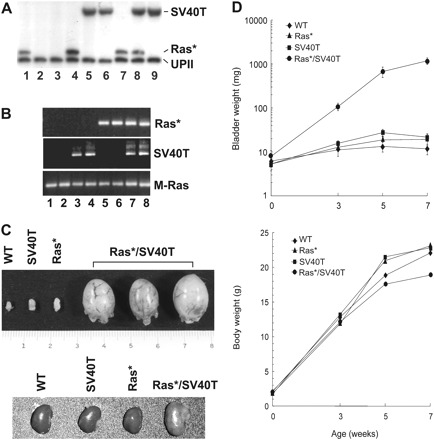
Rapid tumor formation from urothelial cells expressing both Ras* and SV40 large T antigen (SV40T). (A and B) Generation of double transgenic mice expressing both Ras* and SV40T. (A) Genotyping by Southern blotting of a mouse litter showing the generation of (i) single transgenics containing the Ras* transgene (lanes 1, 4 and 7); (ii) single transgenics containing the SV40T transgene (lanes 5, 6 and 9); (iii) double transgenics containing both Ras* and SV40T transgenes (lane 8) and (iv) non-transgenic mice containing neither transgene (lanes 2 and 3). UPII denotes the restrictive digestion fragment from the endogenous mouse UPII gene. (B) Reverse transcription–PCR assay of urothelial expression of Ras* and/or SV40T in the various genotypes as shown in (A), establishing that urothelial cells from non-transgenic mice expressed neither Ras* nor SV40T (lanes 1 and 2); those from single transgenics expressed either SV40T (lanes 3 and 4) or Ras* (lanes 5 and 6) and those from double transgenic expressed both (lanes 7 and 8). (C) Gross anatomy of 5-week-old single and double transgenic mice showing that the bladder sizes of the wild-type (WT) and single transgenic mice were hardly distinguishable and that the bladders of the double transgenics were profoundly enlarged. Lower panel: the corresponding kidneys from these mice, showing the hydronephrosis of a double transgenic mouse. (D) Bladder and body weights of single and double transgenic mice. While the body weights did not significantly differ among the different genotypes, the body weights of the double transgenic mice were about 50-fold higher than those of the WT and single transgenics in 7-week-old groups. Values were means ± SD.
