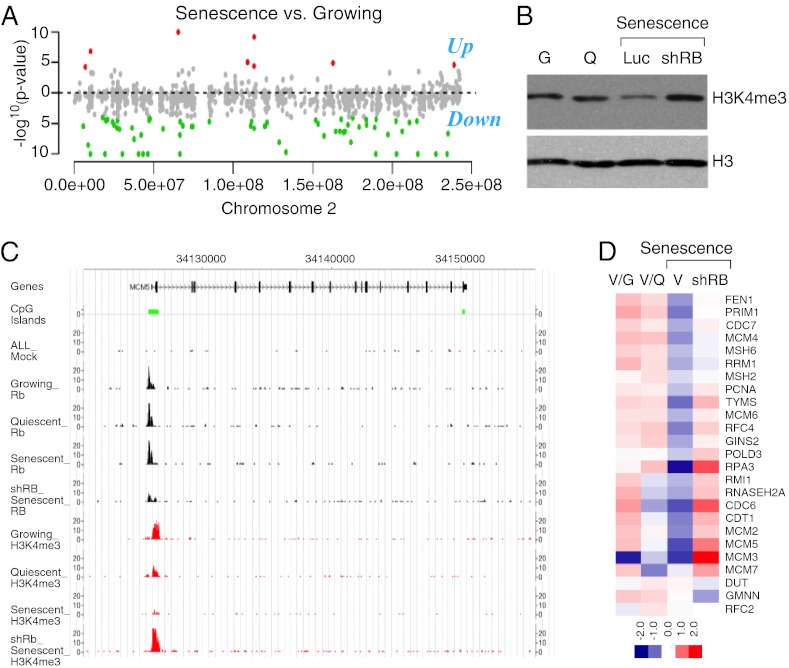
Fig. 2.
The RB tumor suppressor is required for the senescence-associated global and gene-specific loss of H3K4me3. (A) Shown is the log10 of the P values of the difference in H3K4me3 across chromosome 2 of growing vs. senescent cells (green) or senescent vs. growing cells (red). (B) Immunoblots from chromatin-bound fractions of growing (G), quiescent (Q), senescent (shLuc), and RB- deficient senescent cells (shRB) using an antibody that specifically recognizes H3K4me3 or total histone H3. (C) Genome-browser view documenting the loss of H3K4me3 at the MCM5 gene in senescent cells but not growing, or RB-deficient (shRB) senescent cells. (D) Heatmap representing the relative enrichment for H3K4me3 at the promoter of a subset of RB-regulated genes in growing (G), quiescent (Q), senescent (V), and RB-deficient senescent (shRB) cells.