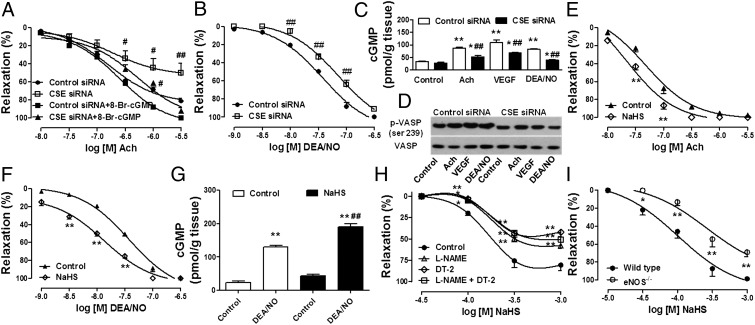
Fig. 5.
Requirement of simultaneous production of H2S and NO in vasorelaxation. Cumulative-concentration response curves to acetylcholine (A) or DEA/NO (B) were performed in aortic rings incubated in isolated organ baths following siRNA-mediated silencing of CSE. ##P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA. To test the effect of cGMP elevation on acetylcholine induced vasorelaxation, cell-permeable cGMP (8-Br-cGMP) was applied at 10 μM concomitantly to cumulative acetylcholine administrations. (C) Aortic rings subjected to CSE gene silencing were stimulated with acetylcholine (1 μM), DEA/NO (0.1 μM), or VEGF (50 ng/mL) for 15 min. At the end of the incubation time, cGMP was extracted and measured by enzyme immunoassay. **P < 0.01 vs. control; ##P < 0.01 vs. corresponding control siRNA. (D) Following CSE gene targeting (siRNA), aortic rings were incubated in Krebs–Henseleit buffer at 37 °C and stimulated with acetylcholine (1 μM, 15 min), DEA/NO (0.1 μM, 15 min), or VEGF (50 ng/mL, 15 min). Tissue lysates were analyzed by SDS/PAGE. PVDF membranes were blotted by using rabbit polyclonal antibodies against phosphorylated (ser 239) or total VASP. (E) Aortic rings were incubated with NaHS 30 μM on PE-induced stable tone. Concentration response curves to acetylcholine (E) or DEA/NO (F) were performed. In these settings, NaHS enhances the vasorelaxant properties of endothelium-derived or exogenously applied NO. **P < 0.01 vs. control. Similarly, 15-min exposure of aortic rings to a low concentration of NaHS (30 μM) enhanced DEA/NO-induced elevation of intracellular cGMP as assessed by enzyme immunoassay (G). (H) Aortic rings were mounted in organ baths, pretreated with vehicle, l-NAME (100 μM), DT-2 (1 μM), or l-NAME + DT-2 on basal tone for 30 min. Rings were then challenged with PE (1 μM), and concentration response curves to NaHS were performed on stable tone. *P < 0.05 and *P < 0.01 vs. control. (I) Aortic tissues were dissected from wild-type and eNOS−/− mice and placed in isolated organ baths under a resting tension of 1.5 g. Following a stabilization period, aortic rings were challenged with PE (1 μM), and cumulative concentration response curves to NaHS were performed. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. wild type.