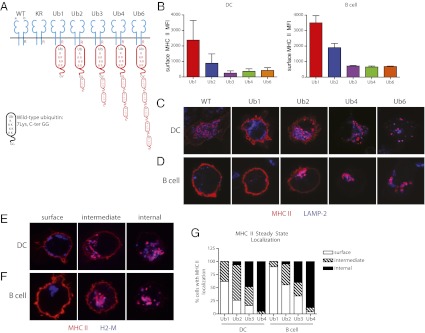
Fig. 4.
Surface expression and localization of MHC II synthetic Ub chains in DCs and splenic B blasts decrease with increasing Ub chain length. (A) Diagram of MHC II: wild-type and Ub chain conjugates. Mutations (red) include a K > R mutation in MHC II β-chain, seven K > R mutations in Ub, and a C-terminal G > V mutation in Ub. (B) MFI of surface-bound MHC II in transduced MHC II β-chain−/− BMDCs (Left) and splenic B blasts (Right). Data are expressed as mean and SEM. (C–F) Confocal microscopy of transduced BMDCs (C and E) and B blasts (D and F). (C and D) Steady-state localization of MHC II in BMDCs and B cells expressing wild type, Ub1, Ub2, Ub4, and Ub6. (E and F) Ub3-expressing BMDCs and B cells exhibit a heterogeneous population of MHC II localization: all surface, all internal, and intermediate between the two extremes. Cells were bound to coverslips, fixed in PFA, and labeled with anti-MHC II antibody TIB120 (red) and lysosomal marker LAMP-1 or H2-M (blue). (G) Quantification of MHC II localization. Transduced BMDCs and B cells were stained with TIB120 and H2-M, then scored for MHC II localization: all surface, both surface and internal, or all internal. n = 50.