Figure 2.
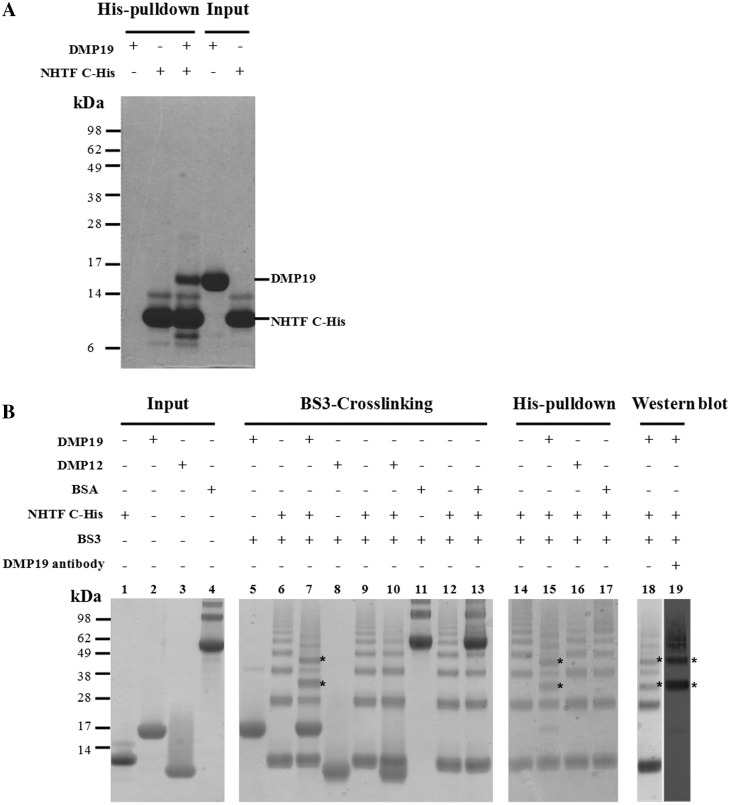
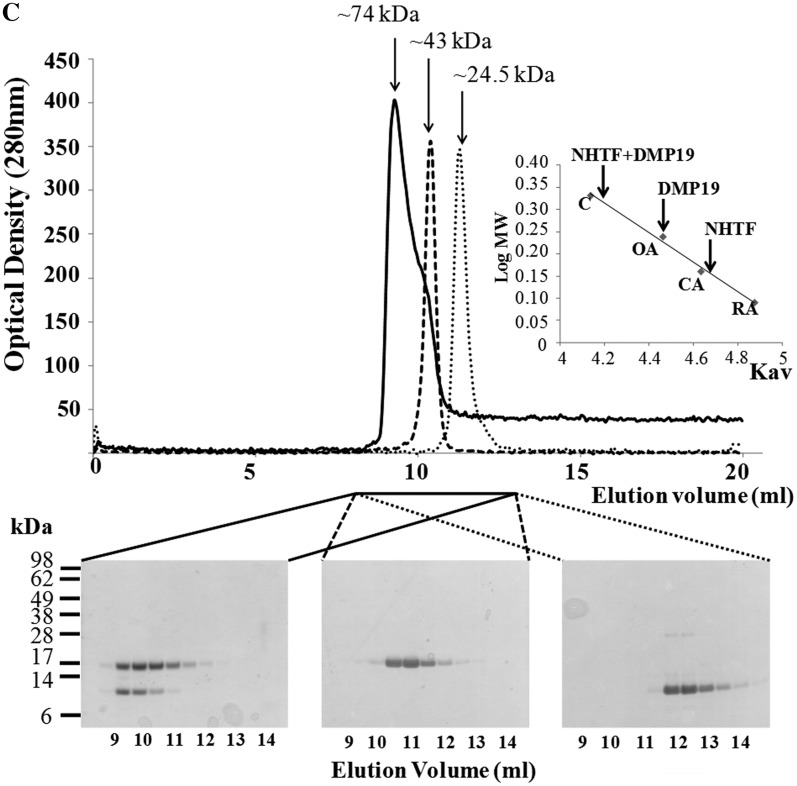
His-pulldown, BS3 cross-linking assays, and gel filtration all confirm that DMP19 and NHTF interact. (A) In this His-pulldown assay, DMP19 without any tag was used as prey and C-terminal His6-tagged NHTF transcription factor (NHTF C-His) was used as bait. DMP19 was pulled-down by NHTF C-His. (B) A BS3 cross-linking assay was carried out to further confirm the interaction between DMP19 and NHTF C-His. NHTF C-His was co-incubated separately with DMP19 and two negative controls (BSA, pI 5.8 and DMP12, pI 4.5). After the addition of BS3, shifted bands that indicated protein–protein cross-linking were only seen in the DMP19/NHTF C-His reactions (lanes 7, 15, 18 and 19); the shifted bands are marked with an asterisk. NHTF C-His was pulled down using Ni-NTA beads, and cross-linked DMP19/NHTF C-His was found in lane 15. The presence of DMP19 in the shifted bands was confirmed by using anti-DMP19 antibody (lane 19). The presence of DMP19 and NHTF C-His in the same shifted bands of this experiment was further confirmed by western blot analysis using anti-DMP19 and anti-NHTF antibodies (Supplementary Figure S3). (C) The molecular weights of DMP19, NHTF and DMP19/NHTF complex were measured by gel filtration on a Superdex 75 HR 10/30 column monitored at 280 nm. The standard proteins conalbumin (C; 75 kDa), ovalbumin (OA; 43 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (CA; 29 kDa) and RNase A (RA; 13.7 kDa) were fractionated on the same column and used to generate a plot of Kav against log MW (inset). The Kav of each target protein (DMP19, NHTF and DMP19/NHTF complex) was then used to find its molecular weight.