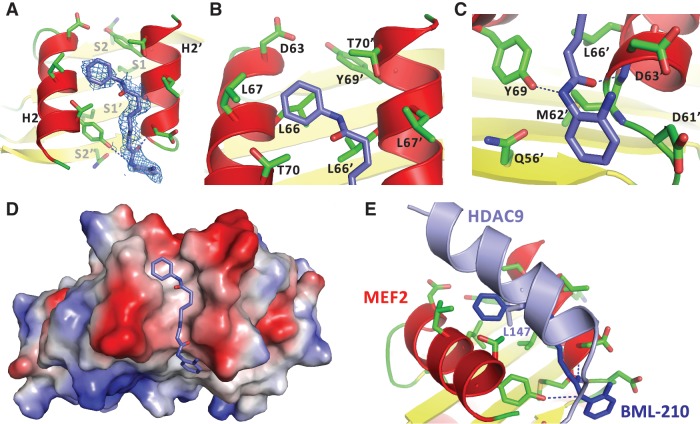
Figure 3.
Structural characterization of the binding of BML-210 to MEF2A. (A) Electron density (blue mesh) matching the shape of BML-210 (blue stick) was identified in the hydrophobic pocket of MEF2 (red and yellow ribbon). (B) The phenyl group of BML-210 is surrounded by a number of hydrophobic residues of MEF2. (C) The 2-aminophenyl group of BML-210 interacts with a number of residues on MEF2. (D) A surface representation showing that the methylene groups of the octanediamide fit snugly between helix H2 of the two MEF2 monomers and that BML-210 adopts an extended conformation to bind the surface groove of MEF2. Positive and negative surface potentials are indicated by red and blue, respectively. (E) Structural superposition using MEF2 as the reference showing that BML-210 and HDAC9 share the same binding site on MEF2 and that the synthetic compound mimics some of the binding interactions of the natural ligands.