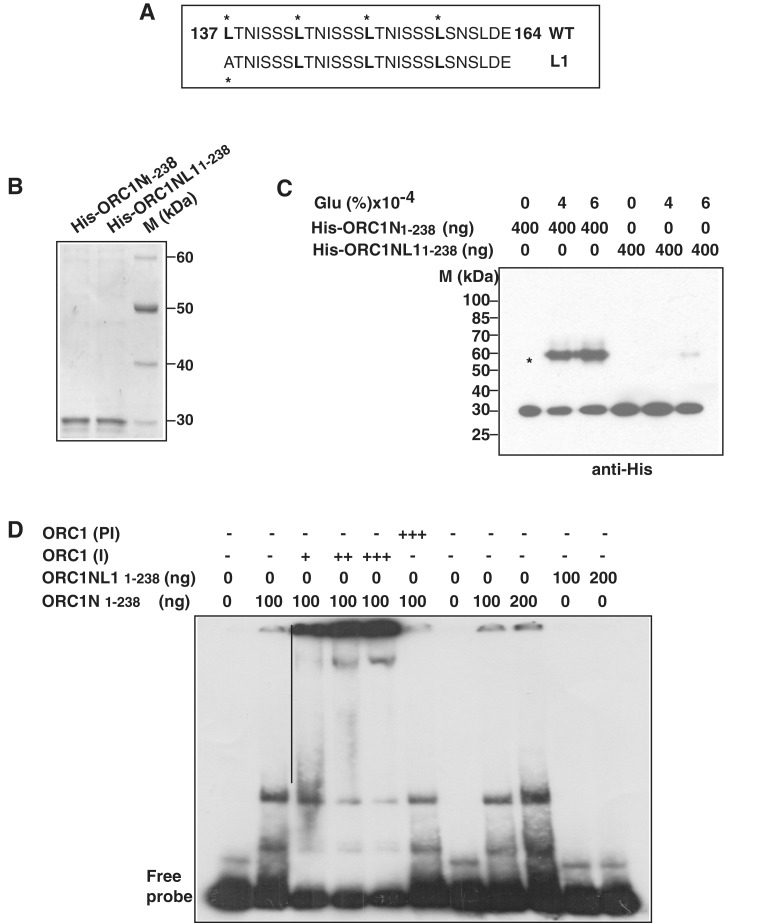
Figure 4.
The leucine heptad repeat in PfORC1N1–238 is essential for oligomerization and DNA binding. (A) The putative leucine heptad repeats of PfORC1N1–238. The leucine at every seventh position is marked. L1 shows the mutation at the first leucine residue. (B) Purification of His6-tagged PfORC1N1–238 wild-type and PfORC1NL11–238 mutant. (C) Cross-linking of His6-PfORC1N1–238 and His6-PfORC1NL11–238 using glutaraldehyde followed by western-blot analysis using anti-His antibodies shows strong dimerization of the wild-type protein (asterisk) but not for the mutant protein. (D) Specificity of ORC1N for DNA binding. EMSA was performed using purified PfORC1N1–238 and radiolabeled telomere DNA probe followed by supershift using different amount of antibodies against PfORC1N (I) (lanes 3–5; 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 µl, respectively) or pre-immune sera (PI) (lane 6, 1.5 µl). The straight line shows the positions of different supershifted bands. EMSA using PfORC1N1–238 wild-type and mutant form shows that the wild-type but not the mutant form binds to telomeric DNA (lanes 7–11). Two different concentrations of each protein (100 and 200 ng) were used.