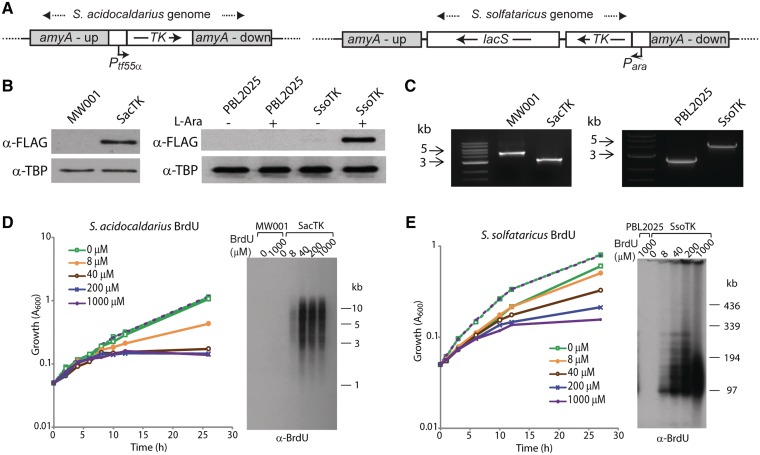
Figure 1.
Sulfolobus acidocaldarius and S. solfataricus strains expressing FLAG-tagged TK from P. aerophilum incorporate BrdU into genomic DNA. (A) The TK-FLAG gene, expressed from a tf55α promoter, was integrated into the amyA locus of S. acidocaldarius MW001 using a ‘pop-in pop-out’ approach. Double crossover homologous recombination was used to integrate the TK-FLAG gene, expressed from an arabinose-inducible promoter, into the amyA locus of S. solfataricus PBL2025. The lacS marker confers growth to PBL2025 in lactose minimal media. The regions flanking the amyA gene are labelled amyA-up and amyA-down. (B) Western blot analysis of whole cell extracts from exponential cultures of parental strains (MW001 or PBL2025) and TK-FLAG integration strains (SacTK and SsoTK) using an anti-FLAG antibody, and anti-TBP antibody as a control. S. solfataricus cultures were grown in the absence or presence of 0.4% l-arabinose (l-Ara). (C) PCR amplification across the amyA locus using genomic DNA template generated 4.8 and 2.7 kb products in the parental strains MW001 and PBL2025, respectively, and 3.2 and 4.1 kb products in the mutant strains SacTK and SsoTK, respectively, indicating replacement of amyA with the tf55α-TK-FLAG constructs. (D) MW001 (dashed lines) and SacTK (solid lines) cells were grown in medium containing the indicated concentrations of BrdU and growth was monitored by A600. Genomic DNA was extracted from 6 h samples, digested with PstI and separated by electrophoresis. DNA was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with an anti-BrdU antibody. (E) PBL2025 (dashed lines) and SsoTK (solid lines) cells were grown in medium containing 0.4% l-Ara and the indicated concentrations of BrdU, and growth was monitored by A600. Genomic DNA was extracted from 12 h samples, digested with EagI and separated by PFGE. DNA was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with an anti-BrdU antibody.