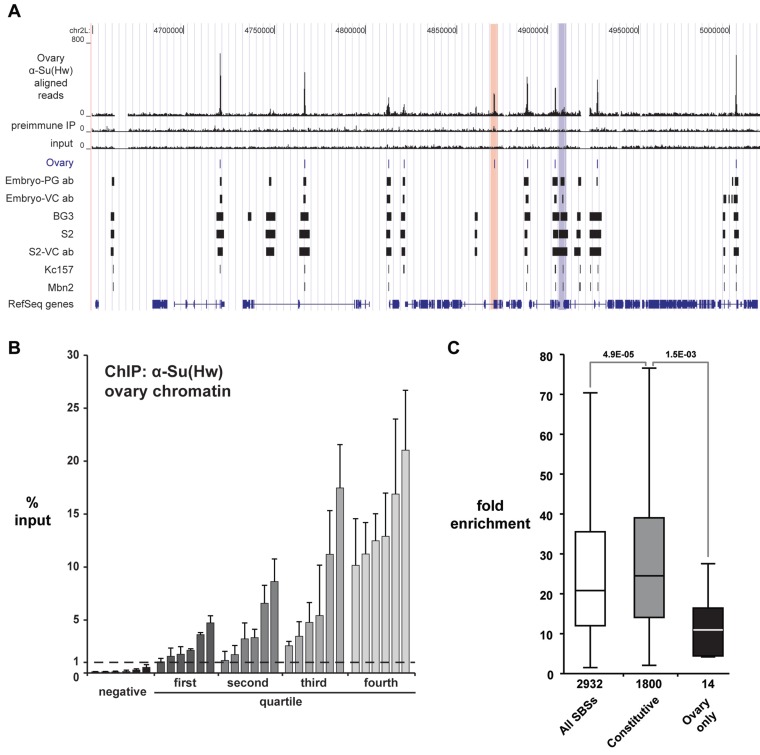
Figure 1.
ChIP-Seq analysis of SBSs in the ovary. (A) Shown is a UCSC Genome Browser view of a representative 360 kb region of chromosome 2L. Several tracks are shown, including Su(Hw)WT ovary ChIP-Seq reads, the pre-immune serum IP control reads, and the input chromatin control reads. The ovary peaks (1% FDR) defined from our data are compared to SBSs identified in (33,34). These latter datasets include peaks identified in embryos using the PG or VC antibody and four cell lines (BG3, S2, Kc157 and Mbn2). Examples of ovary-gained and ovary-lost sites are highlighted (red and blue bars). (B) Shown are data from validation studies of SBSs identified in ChIP-seq. ChIP-qPCR was completed on two biologically independent chromatin isolations, distinct from that used for ChIP-seq. SBSs are arranged into four quartiles based on the level of Su(Hw) occupancy predicted from ChIP-Seq data. Six randomly chosen SBSs from each quartile were tested. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Negative controls represent sites that lack a Su(Hw)-binding motif. These sites were not identified in the ChIP-Seq dataset. (C) Box plot of fold enrichment values of all SBSs identified in the ovary (white), SBSs identified in all genome-wide studies (constitutive, gray), and SBSs identified only in the ovary dataset (ovary only, black). Boxes represent the 25–75 percentile interval, with the median enrichment indicated by the line. Whiskers represent the non-outlier range. P-values of Student’s t-test are indicated.