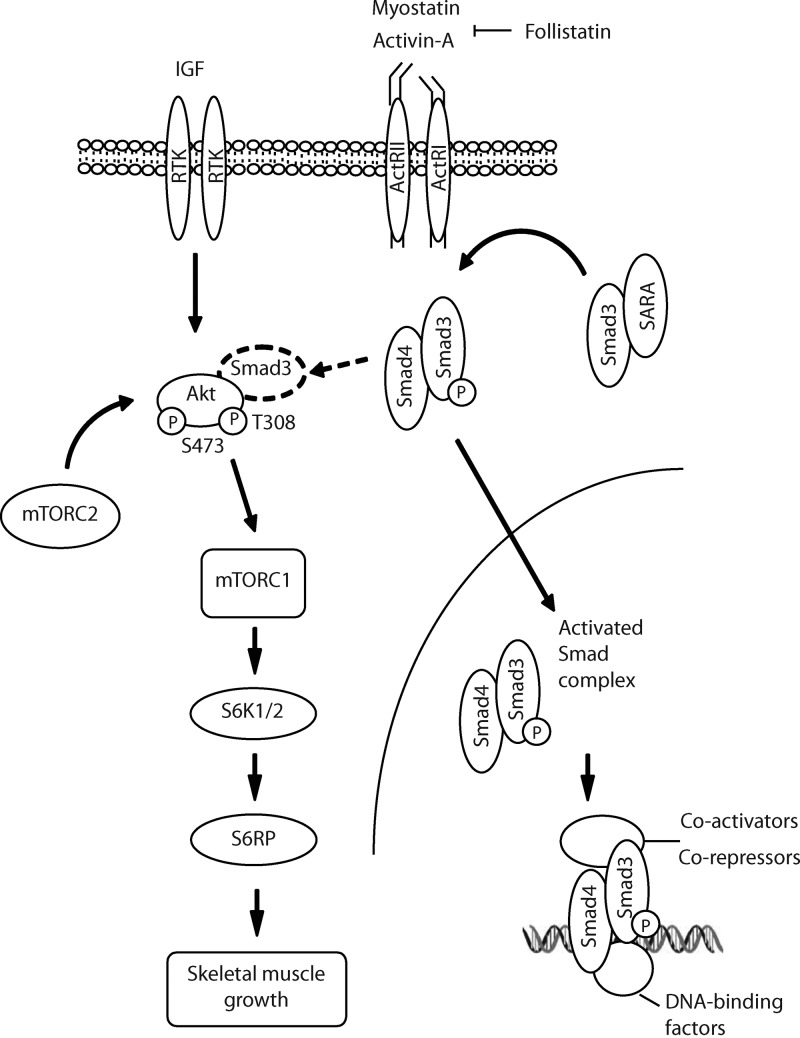
Figure 6.
Proposed model of signaling associated with Fst-mediated skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Fst inhibits the activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway by binding to multiple extracellular ligands including myostatin and Activin A. Inhibiting the actions of myostatin and Activin A diminishes phosphorylation of Smad3, which alters the transcription of Smad target genes, and potentiates Akt/mTOR signaling that stimulates protein synthesis. Increased phosphorylation of Akt contributes to the inhibition of Smad3-dependent signals that otherwise repress muscle growth (arrow with broken line), thereby maximizing protein synthesis networks regulated by Fst.