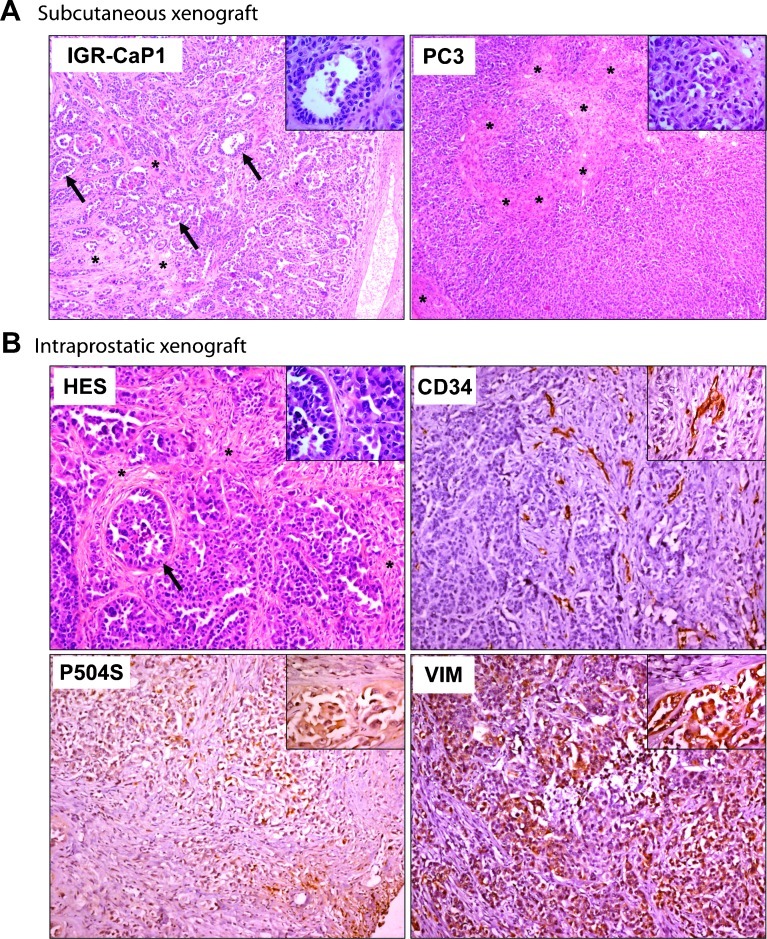
Figure 2.
IGR-CaP1 tumors reconstitute prostate adenocarcinoma. IGR-CaP1 cells were injected into mice both subcutaneously (A) or intraprostatically (B). Magnification, x50; insert, x400. (A) Comparison of HES staining of tumor sections between IGR-CaP1 and PC-3 tumors revealed a glandular differentiation with acini (shown with arrows and in insert) in IGR-CaP1 tumor that is absent in PC-3 tumors. (B) HES staining of tumor sections of orthotopically implanted IGR-CaP1 cells showed more undifferentiated tumors with abundant stroma. Immunohistochemical staining of the endothelial cell marker CD34 showed a high microvessel density within the stromal regions. Vimentin (VIM) revealed the invasive potential of the tumor. Markers corresponding to AMACR (P504S) confirmed the prostate origin of the tumor. Magnification, x100; inserts, x400. Arrows indicate the presence of acini and asterisks show stromal regions.