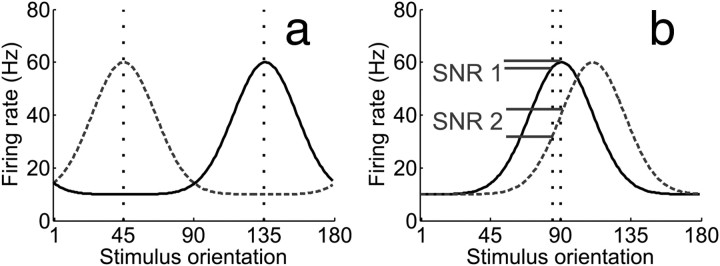
Figure 1.
a, Target (135°) and distracter (45°) orientations are marked by vertical dashed lines. During a coarse discrimination with low target/distracter similarity, neurons tuned to the behaviorally relevant feature should be the target of attentional gain, given their large signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). However, (b) during a fine discrimination, off-target neurons that flank the behaviorally relevant feature theoretically carry more information, yielding a higher SNR. Target (90°) and distracter (92°) orientations are marked by vertical dashed lines. (Adapted with permission from Navalpakkam and Itti, 2007).