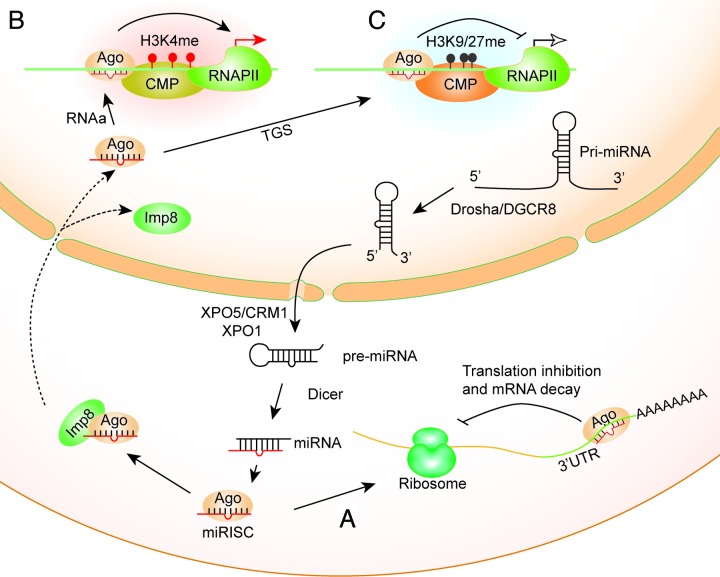
Figure 1. Actions of miRNAs in the nucleus. Canonical miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) into primary miRNA transcripts (pri-miRNAs), which are further processed into miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs) in the nucleus by Drosha/Dgcr8. Pre-miRNAs are then exported to the cytoplasm by Exportin 5 (XPO5)/CRM1 and are processed into mature miRNAs by Dicer. One of the strands is preferentially incorporated into the Argonaute (Ago) protein, a component of the miRISC complex. (A) Classical function of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional inhibition by 3 ‘UTR targeting. (B and C) In order for miRNAs to function in the nucleus, Ago-miRNA complex is imported into the nucleus by binding to Importin 8 (Imp8). Promoter-targeted miRNA complexed with Ago binds to chromosomal DNA sequences or nascent cognate transcripts derived from promoters. During RNAa, recruitment of chromatin modifying proteins (CMPs) leads to increased H3K4 methylation thereby activates transcription at the targeted promoter (B). In TGS, recruitment of CMPs leads to increased H3K9/K27 methylation thereby inhibits transcription at the targeted promoter (C). RNAa: RNA activation; TGS: transcriptional gene silencing; CMPs: chromatin modifying proteins; miRISC: miRNA-containing RNA induced silencing complex

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.