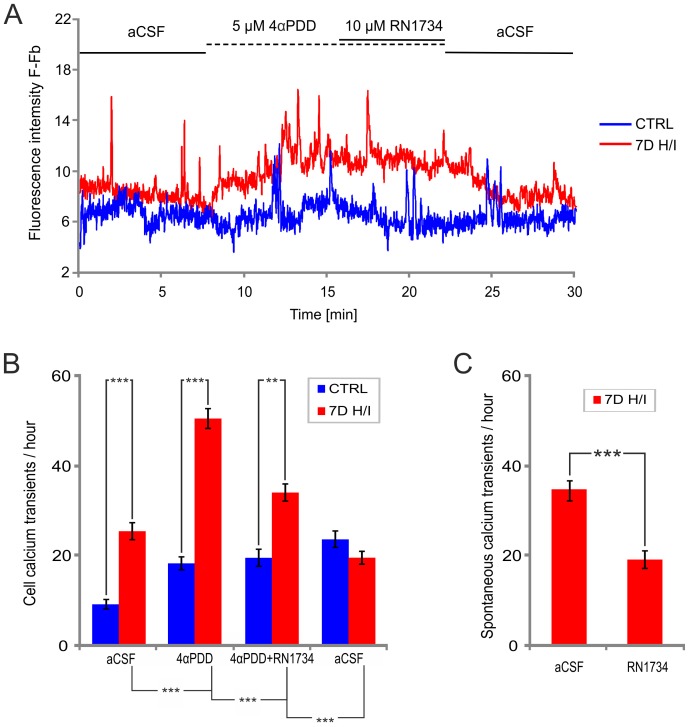
Figure 4. The TRPV4 antagonist RN1734 decreases 4αPDD-induced and spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in astrocytes of the hippocampal CA1 region 7 days after ischemia.
(A) Representative fluorescence traces of hippocampal astrocytes in slices prepared from sham-operated rats (CTRL) and rats 7 days after hypoxia/ischemia (7D H/I) before 4αPDD application (aCSF), during 5 µM 4αPDD application, during the application of 5 µM 4αPDD with 10 µM RN1734 and following washout (aCSF). (B) Histogram of the mean intracellular calcium transients per hour before 4αPDD application (aCSF), during the application of 5 µM 4αPDD, during the application of 5 µM 4αPDD +10 µM RN1734 and following washout in aCSF, in astrocytes in hippocampal slices prepared from the brains of sham-operated rats (CRTL, n = 43) and those 7 days after hypoxia/ischemia (7D H/I, n = 40). (C) Histogram of the mean spontaneous intracellular calcium transients per hour before RN1734 application (aCSF) and during the application of 10 µM RN1734 (RN1734), measured in astrocytes from acute hippocampal slices 7 days after hypoxia/ischemia (7D H/I, n = 10). The values are presented as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA in (B) and a paired t-test in (C); ***p<0.001 extremely significant, **p<0.01 very significant.