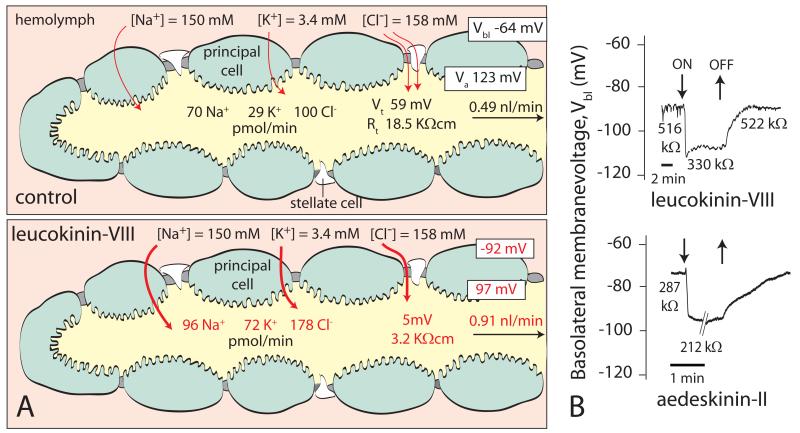
Figure 2.
The effect of insect kinins on isolated Malpighian tubules of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. (A) Leucokinin-VIII, one of the kinins of Leucophaea, significantly increases the rate of fluid secretion by stimulating the transepithelial secretion of both NaCl and KCl. At the same time, leucokinin-VIII depolarizes the transepithelial voltage (Vt) and reduces the transepithelial resistance Rt, Vbl, and Va are respectively the basolateral membrane voltage and apical membrane voltage of a principal cell. Red letters indicate minimum statistical significance at P < 0.05. Data from [17]. (B) Time course of the on/off effects of leucokinin-VIII and aedeskinin-II, one of the kinins of Aedes aegypti. Principal cells of Malpighian tubules were studied by the methods of two-electrode-voltage-clamp [39]. Both kinins depolarize Vbl and decrease the cell-input resistance, reflecting in part the opening of Ca2+ channels in the basolateral membrane [19].