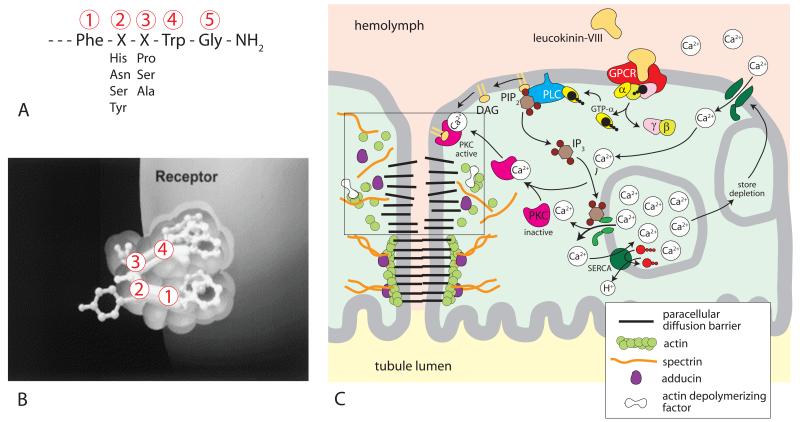
Figure 3.
Kinin signaling to the paracellular pathway of Aedes Malpighian tubules. (A) The active C-terminal amide pentapeptide sequence of insects kinins [68]. (B) Binding of insect kinin to its receptor. The critical C-terminal pentapeptide sequence is thought to fold for reaching into the receptor pocket [42, 69]. (C) G protein-coupled receptor signaling of leucokinin-VIII to septate junctions. Binding of leucokinin-VIII to its receptor increases intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. The Ca+2 activation of protein kinase C phosphorylates adducing, which destabilizes the cytoskeleton associated with the paracellular pathway. The destabilization opens paracellular diffusion barriers (box). GPCR, G protein coupled receptor; α, β, γ, subunits of G protein; GTP guanosine-5′-triphosphate; PLC, phospholipase C; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-triphosphate; IP3, inositol triphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; SERCA, sacra/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase.