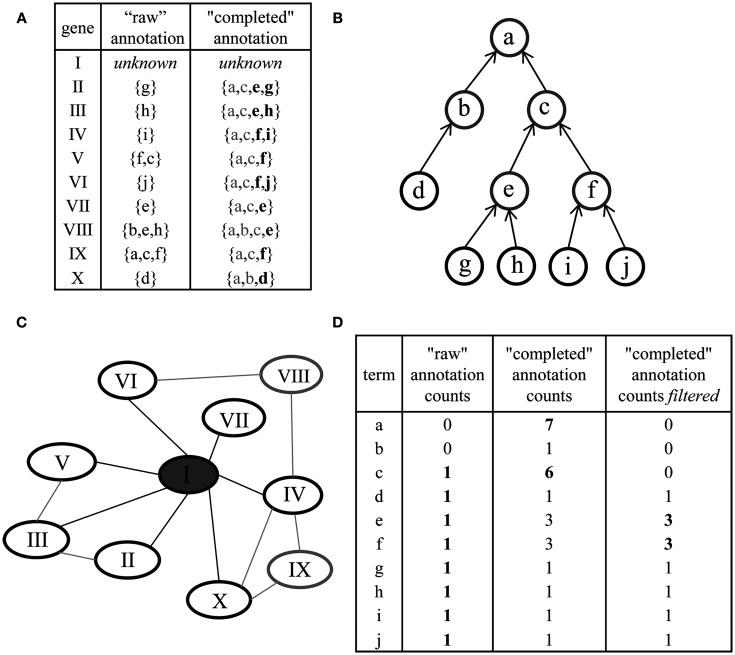
Figure 9.
Preprocessing of ontologies and network-based gene function prediction by majority voting. (A) The original annotation of genes (“raw” annotation) and corresponding concepts (denoted by letters) is extended for each gene by including all parent concepts. The latter is referred to as “completed” annotation. Additional filtering can be performed to remove concepts annotated by many genes (gray letters). (B) Parent terms can be readily obtained by traversal of the ontology structure (a node represents a concept, an arrow an is a or part of relationship among concepts; terminal or leaf concepts are denoted in black). (C) Gene function prediction of the unknown gene, denoted by I, by using the majority voting approach: the annotation of all immediate neighbors in a co-expression network (black ellipses) is considered. (D) Deriving a prediction for the gene I by ranking the annotation obtained through its neighbors. By using the raw annotation, unambiguous prediction cannot be derived (left column); the “completed” annotation aids in deriving meaningful predictions by considering concepts intermediate in the hierarchy (e.g., concept c, middle column); additional filtering (right column) further improves the prediction (“optimized ontology”).