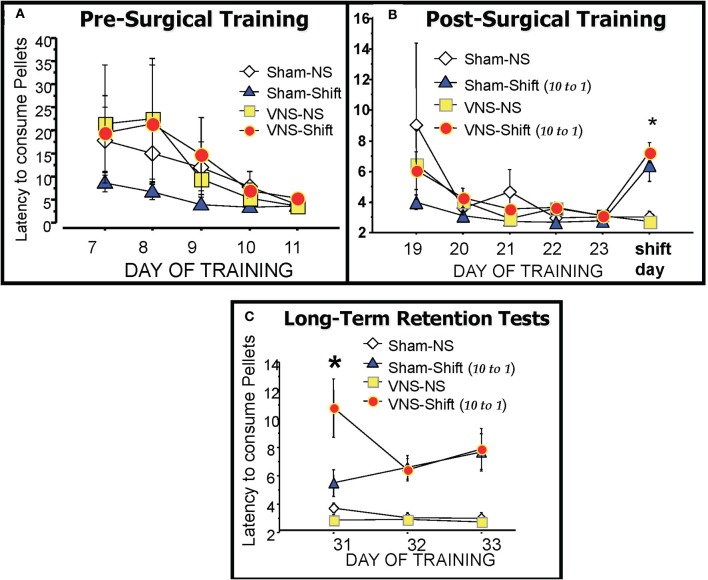
Figure 2.
The runway latencies of each training group during pre-surgical training (A), post-surgical training (B) and during the three days of retention testing (C). There were no significant differences between groups during the training periods. The reduction in reward magnitude from 10 pellets to only 1 pellet on the day of the Shift resulted in significantly longer latencies in the two shifted groups (Sham-Shift and VNS-Shift) relative to the Non-Shifted controls (Sham-NS and VNS-NS). The VNS-Shift group received vagal stimulation after the six training trials with the reduced reward whereas the Sham-Shift group was connected to the stimulator but no current was applied. Retention for the frustrating experience of reward reduction produced by the Shift was assessed one-week later on three daily retention tests. Animals in the vagal stimulation Shift group displayed enhanced retention on the 7 day delayed retention test as evidenced by their continued long latencies to traverse the maze to consume the reduced reward of 1 pellet. Details included in the text.