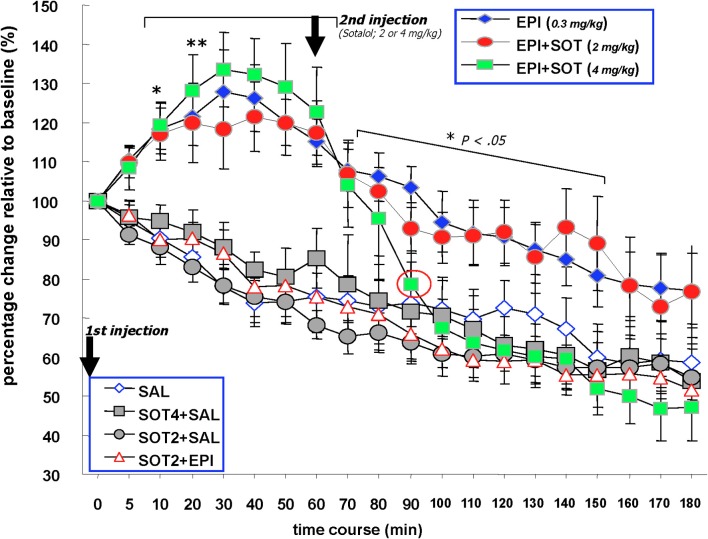
Figure 3.
The effects of systemically administered saline, epinephrine (0.3 mg/kg), sotalol (2.0 or 4.0 mg/kg) or the combination of epinephrine and sotalol on vagal nerve firing in Millivolts. Animals received sotalol 15 min prior to minute (0) and epinephrine at this time point. The first injection at 0 min. Two of the epinephrine injected groups received a second injection at 60 min that consisted of sotalol at 2 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg. One of the saline injected groups received a second injection at 60 min of sotalol at 4 mg/kg. The EPI, EPI + SOT2, and EPI + SOT4 groups exhibited significant increases in vagal firing discharge above baseline for 10–60 min post-epinephrine injection. For the remaining time of recording, vagal activity in the EPI and EPI + SOT2 groups gradually decreased to approximately 20% above basal values. In contrast, vagal activity in the EPI + SOT4 group dropped steeply at 40 min post-sotalol injectionand was reduced by approximately 50% relative to baseline at the end of recording. Neural activity recorded in the form of Millivolts from the vagus nerve in the SAL, SAL + SOT4, SOT2 + EPI, and SOT2 + SAL groups decreased over time with a reduction of approximately 50% relative to baseline at the end.