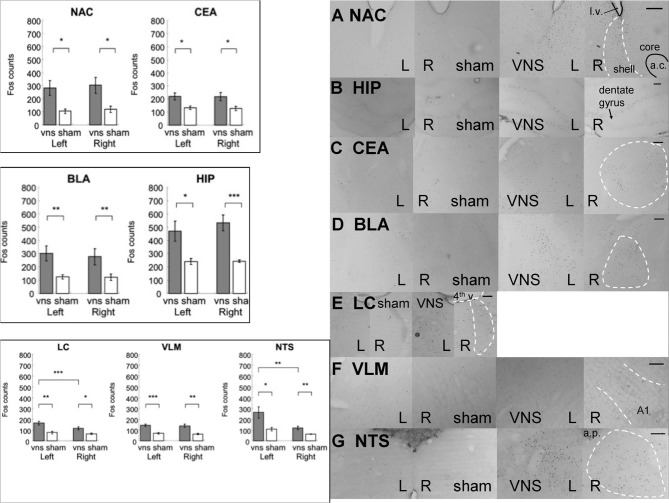
Figure 5.
Electrical stimulation of the left vagus nerve significantly increased Fos-like immunoreactivity in each of the examined brain regions bilaterally: NAC, CEA, BLA, HIP, LC, VLM and NTS. In addition, the stimulation also induced an ipsilateral predominance of Fos expression in the LC and NTS. (*, **, and *** denotes significant difference between the compared groups with a p-value less than 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively). Photomicrographs of Fos labeling in the NAC (A), HIP (B), CEA (C), BLA (D), LC (E), VLM (F), and NTS (G) following sham or vagus nerve stimulation. Scale bar = 200 um. (l.v.: lateral ventricle; a.c.: anterior commisure; shell: the shell region of the nucleus accumbens; core: the core region of the nucleus accumbens; 4th v.: the fourth ventricle; a.p.: area postrema.