Figure 1.
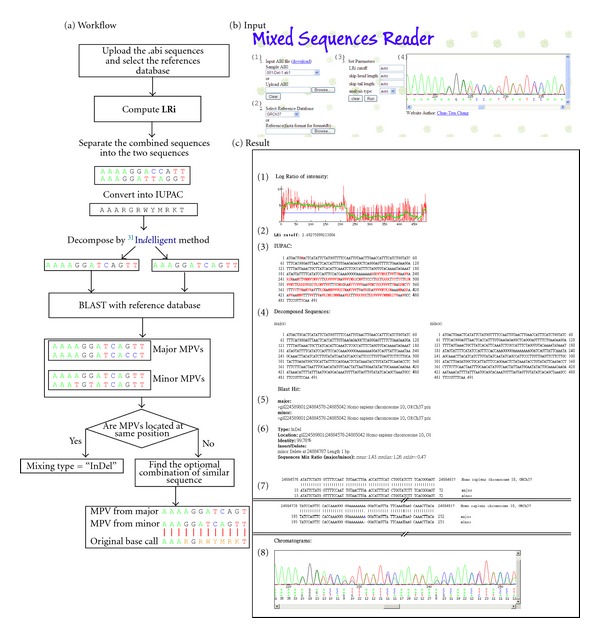
Workflow and user interfaces (input and result output) of the Mixed Sequences Reader (MSR). A flowchart describing the MSR workflow is shown in the left-side panel (a); the input interface of MSR is shown in the right-side panel (b); the result output is shown in panel (c). To input data, users can upload .abi sequences (b-1) and select the desired reference sequences (b-2). MSR defines an LRi (log ratio of intensity) value for each sequence as the log ratio of the two intensities of the combined signal peaks. On the basis of the smooth LRi curve (c-1), the LRi can be calculated (c-2); this value is used to separate the combined sequences into two sequences and then convert them into IUPAC code (c-3). The IUPAC codes are decomposed by Indelligent method into major and minor sequences (c-4). The major and minor sequences are BLASTed against a set of reference sequences to obtain the major and minor most possible variances (MPV) (c-5). If the MPVs are located at same position, the variant type is defined as an “indel”; if they are at different positions, the variant is defined as a “mixed” type (c-6). The variant type is then reported (c-7). The chromatographs of the analyzed sequences are shown in (b-4). The combination of major and minor sequences is shown in (c-8). Users have the option to define the LRi cut-off value, sequence type, and the ignored head and tail sequence lengths (b-3).
