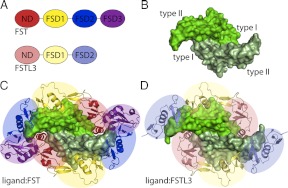
Fig. 1.
Overview of ligand and FST-type structures. A, Domain layouts of FST and FSTL3, which are similar to one another. B, TGF-β ligands are dimers with four surfaces important for type I and type II receptor binding, as indicated. Myostatin is shown as an example. C, The structure of myostatin bound to FST288 [3HH2 (28)]. FST antagonizes signaling by completely surrounding a ligand with two FST molecules, blocking all receptor-binding sites. The ND of FST plugs the type I receptor-binding site, whereas FSD1 and FSD2 cover the type II site. There are additional contacts between the ND of one FST molecule and FSD3 of the other. FSD3 itself does not interact with ligand. D, The structure of myostatin bound to FSTL3 [3SEK (25)]. FSTL3 binds ligands similarly to FST but lacks the ND-FSD3 interaction. Structure figures were rendered using PyMOL (48).