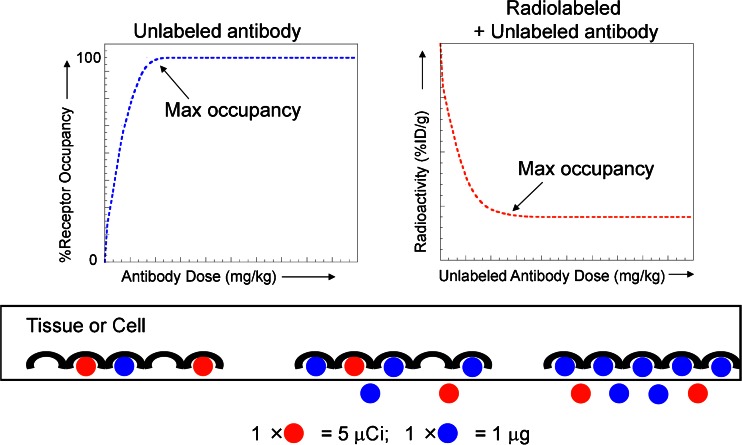
Fig. 2.
Receptor occupancy as it relates to dose in terms of absolute versus radiotracer uptake. In a direct binding model (left), as the dose of total antibody increases, the percent receptor occupancy also increases, approaching 100% or maximum occupancy. In contrast, in a competitive binding model (right), the radiotracer is used as a marker to follow the antibody levels in the tissue. At a fixed dose of radiotracer, radioactivity levels in the tissue decrease with increasing dose of unlabeled antibody due to competitive binding, reaching a bottom plateau at maximum occupancy. The cartoon below the graphs illustrates these concepts at the receptor level, with the unlabeled antibody (measured in micrograms) represented in blue and the radiolabeled antibody (measured in microcuries) represented in red