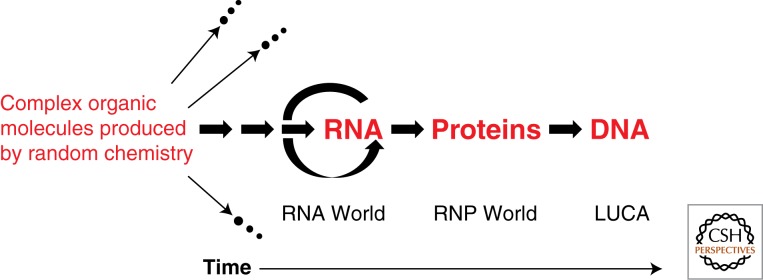
Figure 1.
An RNA world model for the successive appearance of RNA, proteins, and DNA during the evolution of life on Earth. Many isolated mixtures of complex organic molecules failed to achieve self-replication, and therefore died out (indicated by the arrows leading to extinction.) The pathway that led to self-replicating RNA has been preserved in its modern descendants. Multiple arrows to the left of self-replicating RNA cover the likely self-replicating systems that preceded RNA. Proteins large enough to self-fold and have useful activities came about only after RNA was available to catalyze peptide ligation or amino acid polymerization, although amino acids and short peptides were present in the mixtures at far left. DNA took over the role of genome more recently, although still >1 billion years ago. LUCA (Last Universal Common Ancestor) already had a DNA genome and carried out biocatalysis using protein enzymes as well as RNP enzymes (such as the ribosome) and ribozymes.