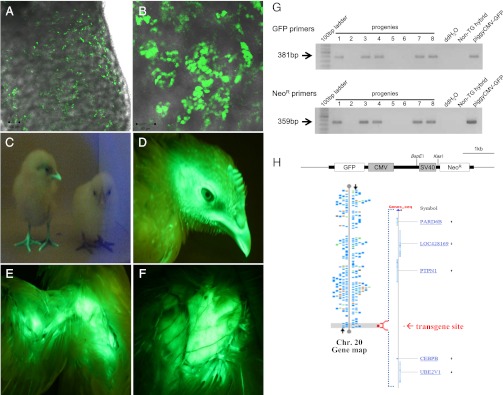
Fig. 2.
Detection of GFP-expressing PGCs in recipient embryonic gonads and GFP-expressing transgenic chickens. Detection of GFP-expressing donor PGCs in recipient testes of 18-d-old (A) and hatched chicks (B) by confocal laser scanning microscope. Fluorescent illustrations of hatched chicks (C, the left chick is transgenic and the right chick is a normal hybrid), and head (D), wing (E), and breast (F) of a 10-wk-old transgenic chicken. Transgenic chickens showed strong GFP expression regardless of age. (G) Genomic PCR analysis of transgenic offspring. Transgenic progenies (lanes 1, 3, 4, 7, and 8) were positive for both GFP primers and NeoR primers. Nontransgenic hybrids from the test-cross were negative control chicks. (H) Identification of the piggyBac GFP transgene site by DNA walking. A transgene was integrated into the distal end of chromosome 20. No functional gene or transcript was found within ∼0.1 Mb of the transgene integration site. Alignment of the transgene-flanking sequences from DNA walking analysis was conducted using the BLAST Assembled Genome Database (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).