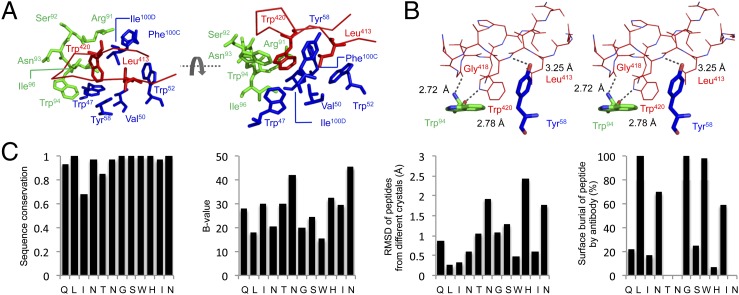
Fig. 3.
Molecular details of antibody binding to the HCV peptide. (A) The Leu413and Trp420 residues on the peptide (red) are shown buried in a hydrophobic depression formed by LC CDR3 residues (green) and by heavy chain FR2, CDR2, and CDR3 residues (blue). (B) Three hydrogen bonds between peptide and antibody also stabilize the interaction, as depicted in wall-eye stereo. Bonds and distances are labeled in black. (C) To further analyze the peptide binding, HCV sequence conservation across 2,161 isolates for this region, crystallographic B-value, rmsd between the two structures, and surface burial by antibody on the peptide are shown. Sequence conservation was taken from the ViPR database (Table S4), whereas the B-values were extracted from the structure and the binding data from ref. 15. The rmsd was calculated on a residue-by-residue basis in PyMOL. Surface burial corresponds to the accessible surface area of each residue on the peptide in the bound structure (P21 structure) normalized by the surface area calculated after the Fab is removed.