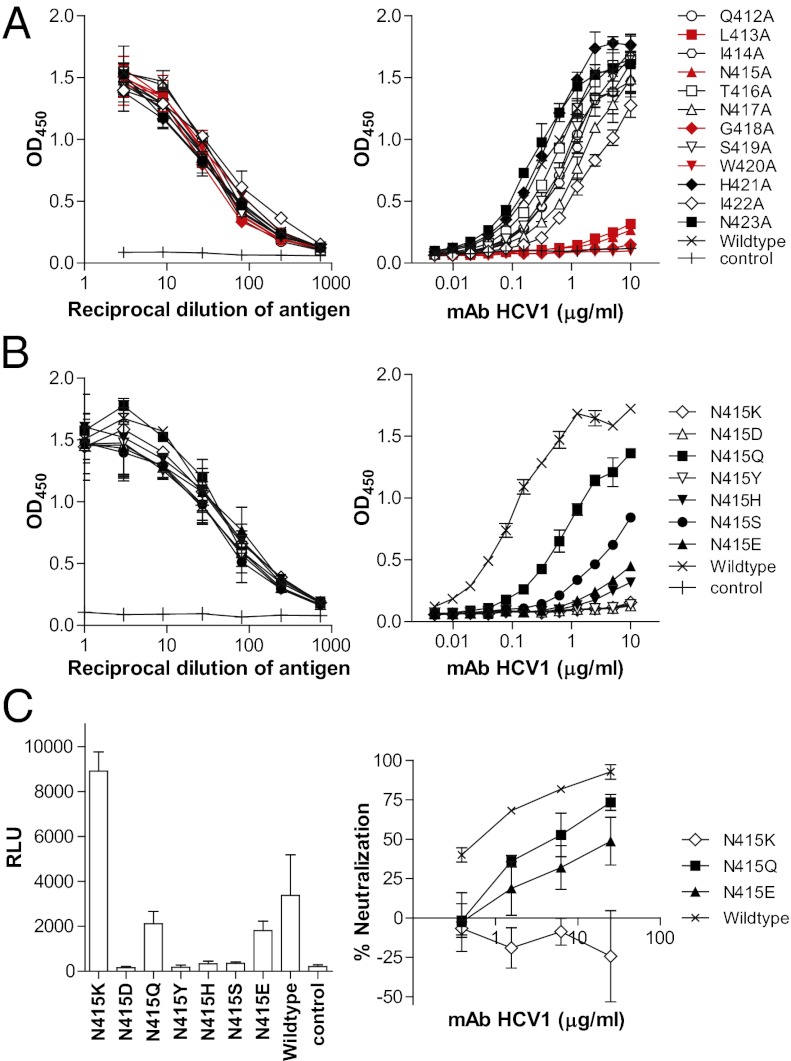
Fig. 4.
Viral escape through substitutions at E2 residue 415. (A) Alanine scanning mapping of the HCV1 epitope. (B) Binding of mAb HCV1 to E1E2 variants with substitutions at position 415, including naturally occurring substitutions and Gln. (A and B) Left: Expression of the variants confirmed by mAb AR2A (1 μg/mL) (19). Right: Binding of mAb HCV to the variants. (C) Escape of mAb HCV1 by substitution at E2 Asn415. HCVpp bearing the specific substitutions were generated as described previously (19). The infectivity of the variant panel was compared according to the activity of the reporter gene luciferase (relative light unit, RLU) (Left). Only the K, Q, and E variants produced HCVpp with significantly higher signals (>10-fold) than the control pseudotype virus generated without E1E2. The sensitivity of these variants to mAb HCV1 was determined by incubating them with serially diluted mAb (Right). The results shown are the means ± SD of two independent experiments of triplicate measurement.