FIGURE 7:
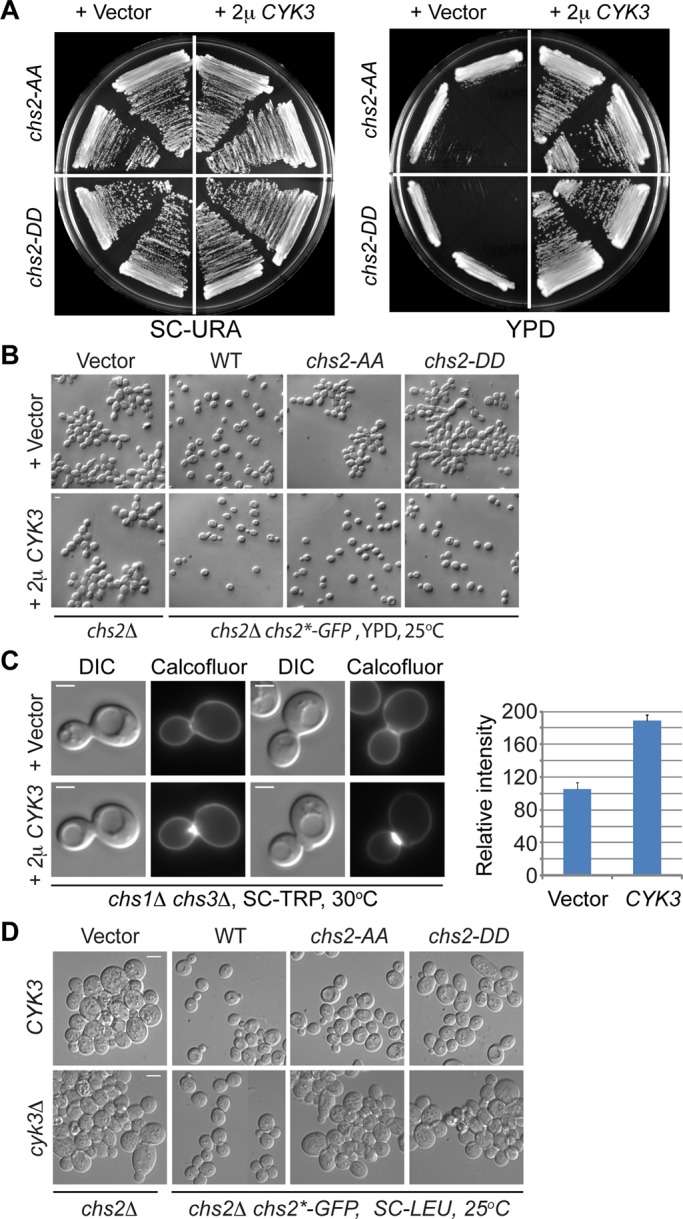
Increased dosage of Cyk3 stimulates Chs2‑dependent chitin synthesis and robustly suppresses the growth and cytokinesis defects of both chs2‑AA and chs2-DD mutants. (A) Multicopy CYK3 suppresses the growth defects of chs2‑AA and chs2‑DD. Strains (YO1543 and YO1544, top half of the plate; YO1550 and YO1551, bottom half of the plate; chs2∆ Chs2*-GFP::LEU2 CDC3-mCherry cells transformed with either an empty vector [pAG426, 2 μ, URA3] or a high‑copy CYK3 plasmid [pAG426-CYK3]) were streaked onto plates containing minimal (SC-URA) or rich (YM-1) media and grown at 25°C for 3–4 d. (B) Multicopy CYK3 suppresses the cytokinesis defects of chs2‑AA and chs2‑DD. Cells of different strains (top, YO1245, YO1246, YO1247, and YO1248; bottom, YO1213, YO1214, YO1215, and YO1216; chs2∆ leu2::LEU2 [pRS305, vector] or chs2∆ Chs2* (WT, chs2‑AA, or chs2‑DD)-GFP::LEU2 cells transformed with either an empty vector [pRS314] or a high‑copy CYK3 plasmid [pBK42]) were grown to exponential phase in rich medium (YM-1) at 25°C and then visualized by DIC microscopy. (C) Increased Cyk3 stimulates Chs2‑dependent chitin synthesis at the division site. Cells (YO1129, YO1130; chs1∆ chs3∆ cells transformed with either an empty vector [p414ADH] or a high‑copy CYK3 plasmid [pBK42]) were grown overnight at 30°C on an SC-TRP plate and then stained for cellular chitin using Calcofluor. The relative amounts of chitin in both strains (Vector, n = 14; CYK3, n = 22) were quantified and presented in the plot. The average intensity for the strain containing the “Vector” was arbitrarily set at 100. The error bar represents SEM. Scale bar, 2 μm. (D) chs2‑AA and chs2‑DD mutations display synthetically enhanced defects with cyk3Δ. Different strains (top, YO1338, YO1339, YO1450, and YO1451; chs2∆ leu2::LEU2 [pRS305, vector] and chs2∆ Chs2* (WT, chs2‑AA, or chs2‑DD)-GFP::LEU2; bottom, YO1209, YO1210, YO1211, and YO1212; chs2∆ cyk3∆ leu2::LEU2 [pRS305, vector] and chs2∆ cyk3∆ Chs2* (WT, chs2‑AA, or chs2‑DD)-GFP::LEU2) were grown to exponential phase in SC-LEU medium at 25°C and then visualized by DIC microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm.
