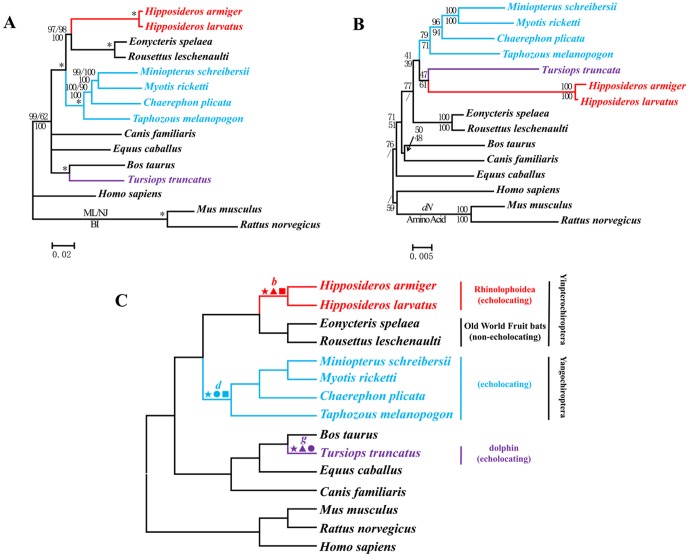
Figure 1. Parallel evolution of Cdh23 in bats and dolphins.
(A) Gene tree of Cdh23 based on nucleotide sequences that is consistent with the species tree. Numbers above the branches are the ML and NJ bootstrap values, respectively. Numbers below the branches are Bayesian posterior probabilities. * indicates all values equal 100. (B) Gene tree of Cdh23 based on nonsynonymous mutations and the amino acid sequences. Numbers along the branches are NJ bootstrap values. (C) Species tree based on previous studies [26]–[28]. Symbols above the branches correspond to amino acid replacements. ★ indicates a parallel amino acid replacement presenting on branches b, d, and g: R204Q. ▴ indicates parallel amino acid replacements presenting on branches b and g: R204Q, D517N, P518A, S639N, N737S, S747T, A1080S, K1141T, S1314T, A1382S, I1673V, N1697D, L1960F, L1974I, A2146V, G2229S, V2427I, T2439R, R2639K, Q2725L, and N3180S. • indicates a parallel amino acid replacement presenting on branches d and g: R204Q. ▪ indicates parallel amino acid replacements presenting on branches b and d: R204Q, R535K, T904I, and V1691I.