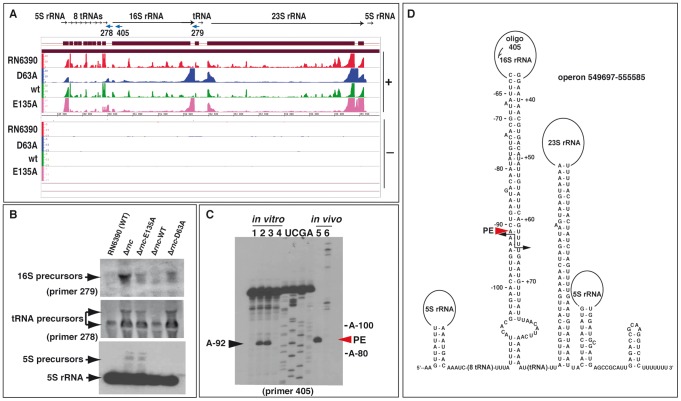
Figure 2. Processing of the rRNA operon by RNase III.
(A) Visualization of RNA fragments identified by deep sequencing in the S. aureus genome using the Integrated Genome Browser (IGB, Affymetrix). For mapping of cDNAs, the genome sequence of strain N315 was used. Sequenced cDNA reads of RNAs obtained from RN6390 strain (negative control) are shown in red, RNA fragments co-immunoprecipitated with the Flag-RNase III D63A mutant in blue, Flag-RNase III wild type (wt) in green, and Flag-RNase III E135A mutant in magenta. (+) Indicates the leading and (−) the lagging strand, respectively. The Y-axis indicates a relative score for the number of mapped reads per nucleotide normalized to the total number of reads. (B) Analysis of rRNA and tRNA precursors in the WT and mutant Δrnc strains. Northern blot analyses were performed with 5′ end-labeled oligonucleotides using RNAs isolated from RN6390 (WT), the Δrnc strain (Δrnc) or the same strain transformed with a plasmid expressing either the E135A mutant (Δrnc-E135A), the wild type (Δrnc-WT) or the mutant D63A (Δrnc-D63A) enzymes. 5S rRNA was detected with a specific DIG-labeled riboprobe, which was produced by in vitro T7 transcription from a PCR product amplified with the oligonucleotides 381/382 (Table S8). Arrows denote the different precursors. (C) Identification of RNase III cleavages in vitro and in vivo using primer extension. The cleavages were mapped in vitro on the 16S rRNA transcript carrying 134 nucleotides at its 5′ trailer region and 100 nucleotides at its 3′ trailer (lanes 1 to 4), and in vivo on total RNA extract (lane 5, WT strain; lane 6, Δrnc strain). RNase III cleavage sites were detected by reverse transcription using the 5′ end-labeled oligonucleotide 405. Lane 1: Incubation control; lanes 2–4: in vitro cleavage assays performed with RNase III WT on pre-16S rRNA using two concentrations of RNase III (lane 2, 0.1 µM; lanes 3–4, 0.2 µM) in the presence of Mg2+ (lanes 1–3) or of Ca2+ (lane 4); lanes U, C, G, A: sequencing ladders corresponded to the RNA sequence. Primer extension was performed on total RNAs prepared from exponential cultures of RN6390 (lane 5) and Δrnc strains (lane 6). (D) Secondary structure prediction of the corresponding pre-rRNA operon. Black arrows show positions of the RNase III cleavages, which were experimentally mapped in the 16S pre-rRNA. PE denotes the primer extension stop (red arrow) obtained from total RNA extract.