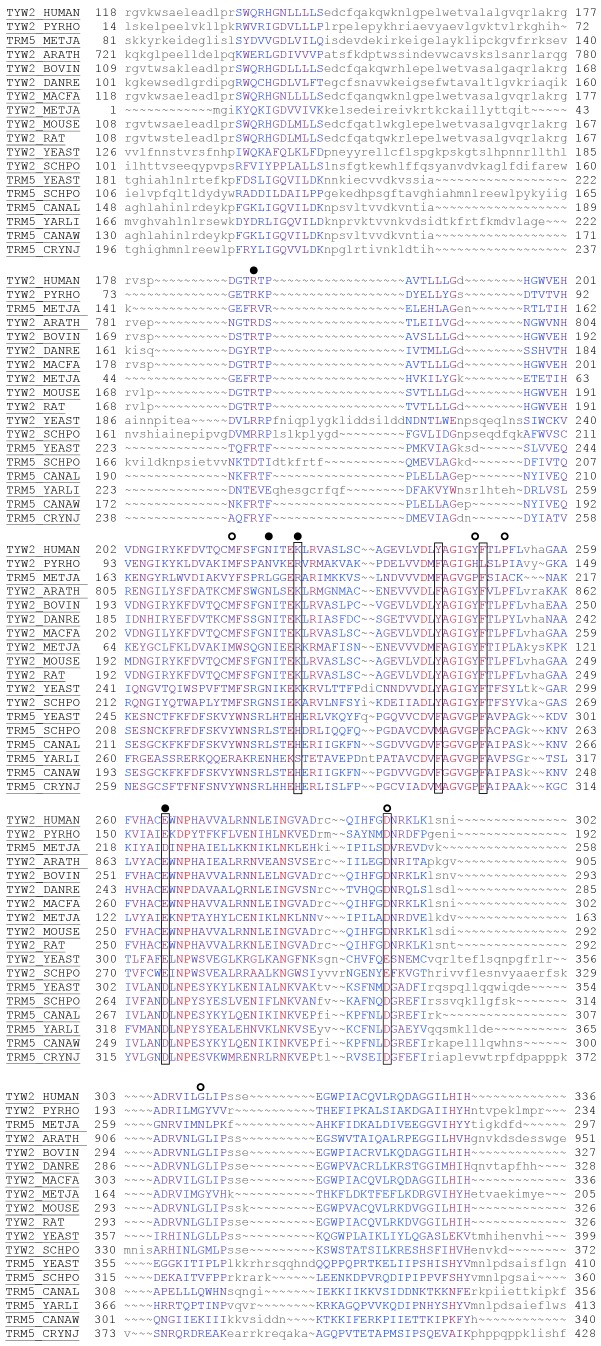
Figure 2. Structure-guided alignment of hTYW2 protein with its homologs.
The alignment shows 18 sequences from the Swiss-Prot (reviewed, manually annotated) subset of the UniProtKB database (www.uniprot.org). The alignment of all 49 sequences in the UniProtKB database, both reviewed (Swiss-Prot) and un-reviewed (TrEMBL) sequences are presented as Figure S2. The alignment was created using the Cn3d tool. The color of the residues reflect the level of conservation with highly conserved residues in red to not conserved residues in blue, and the residues in smaller letters indicate regions of no conservation. This alignment shows only the transferase domain corresponding to residues 118–336 of hTYW2. The sequences are labeled using UniProtKB accessions. The boxes around the positions of five residues in TYW2 HUMAN (K225, Y242, F248, E265 and D293) are to indicate that they were chosen for mutagenesis studies. The circles indicate the nine residues in TYW2 PYRHO that were analyzed by mutagenesis, and those resulting in the severe inactivation of the enzyme activity (>90%) are with filled circles (from Umitsu et al Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 15616–15621). PYRHO: Pyrococcus horikoshii; METJA: Methanocaldococcus jannaschii; ARATH: Arabidopsis thaliana; BOVIN: Bos taurus; DANRE: Danio rerio; MACFA: Macaca fascicularis; METJA: Methanocaldococcus jannaschii; MOUSE: Mus musculus; RAT: Rattus norvegicus; YEAST: Saccharomyces cerevisiae; SCHPO: Schizosaccharomyces pombe; CANAL: Candida albicans; YARLI: Yarrowia lipolytica CANAW: Candida albicans; CRYNJ: Cryptococcus neoformans.