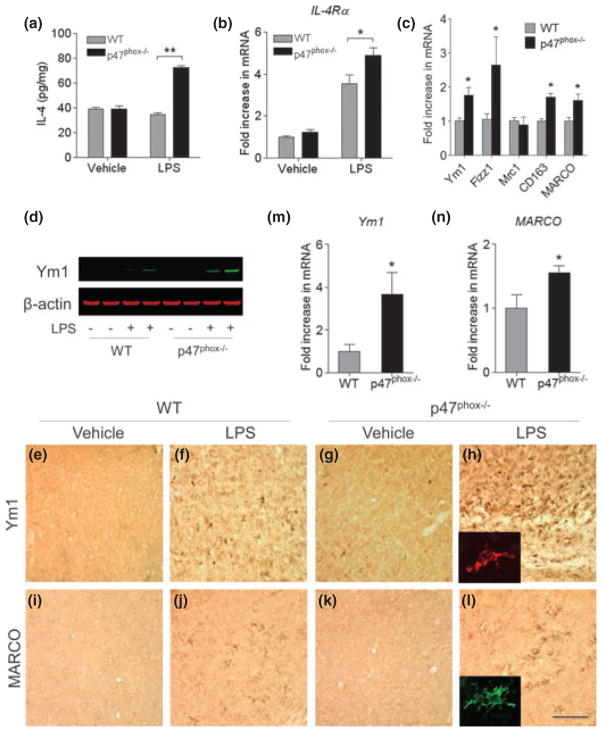
Fig. 3.
Gene deletion of p47phox alters microglia phenotype. (a) ELISA showing production of brain IL-4 in p47phox−/− and WT mice. (b, c) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showing expression of IL-4Rα, Ym1, Fizz1, Mrc1, CD163, and MARCO mRNA (relative to Pgk1) in p47phox−/− and WT mice. Mean ± SEM (n = 6), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (d) Immunoblot showing protein levels of Ym1 in p47phox−/− and WT mice. (e–l) Immunostaining for the Ym1 and MARCO in the hippocampus of p47phox−/− and WT mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. Insets, immunofluorescence staining of Ym1+ and MARCO+ cells in p47phox−/− mice. (m, n) Induction of microglial Ym1 and MARCO. Brain microglia were isolated from WT and p47phox−/− mice at 24 h after LPS challenge and analyzed mRNA expression of Ym1 and MARCO by quantitative PCR. Mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.05. RNA, protein, and tissue samples were prepared from brains of WT and p47phox−/− mice at 24 h after LPS.