Fig. 5.
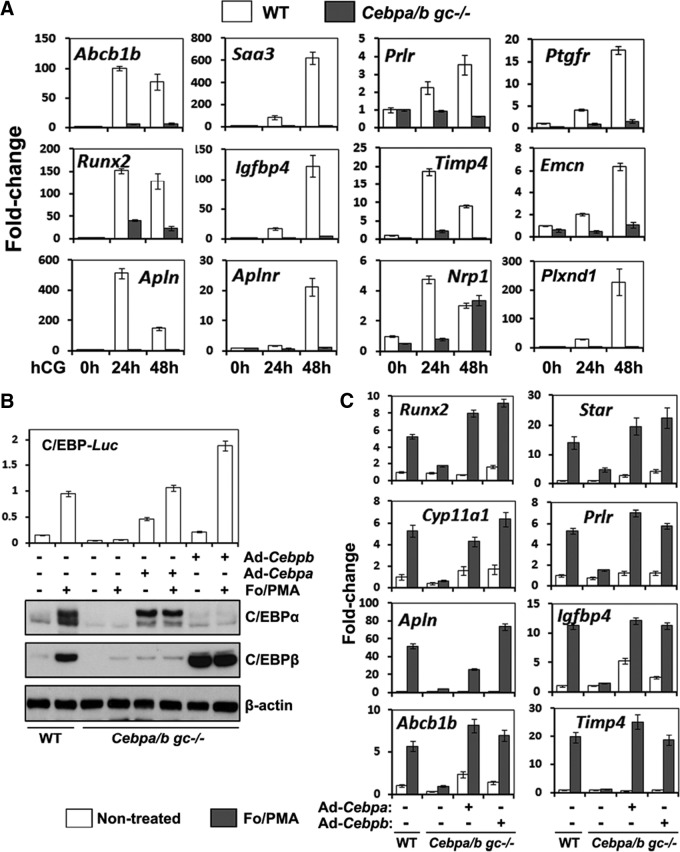
Microarray analyses identify novel C/EBP target genes that regulate ovulation and luteinization. A, Granulosa/luteal cells were isolated from WT and Cebpa/bgc−/− mice before and after hCG treatment (0 h, 24 h, and 48 h) (n = 3 for each treatment). Total RNA was isolated, and the expression levels of indicated genes were determined by real-time RT-PCR. B, GCs were isolated from eCG primed (24 h) 23-d-old immature mice (WT and Cebpa/bgc−/−) and cultured for 24 h. At that time, Cebpa/bgc−/− GCs were washed and infected with adenoviral vectors encoding either C/EBPα or C/EBPβ. After 4 h, the cells were treated with For (10 μm) plus PMA (20 nm) for another 20 h. Western blots show the expression levels of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ proteins. C, GCs were cultured, and infected with adenoviral vectors as in panel B. Then the cells were treated with For/PMA for another 24 h. Expression of indicated C/EBP-target genes was detected by real-time RT-PCR.