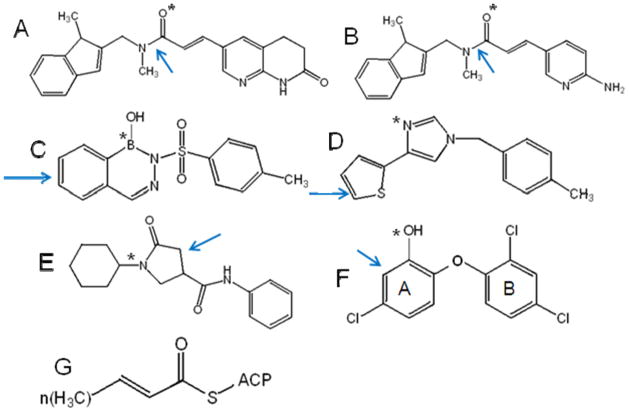
Figure 1.
Structures of known FabI inhibitors with the key binding features highlighted. (A) Indole naphthyridinones,29 (B) aminopyridines,29 (C) Diazaborines,46 (D) disubstituted imidazoles,47 (E) pyrrolidine carboxamide,41 and (F) triclosan.35 The arrows points to the aromatic or delocalized planar moiety that participates in π-stacking interactions with the NAD+ cofactor. The * indicates the hydrogen bond accepting group that can interact with the 2’-hydroxyl group in the ribose ring of NAD+ cofactor. (G) Structure of Trans-2-enoyl-ACP, the natural substrate of FabI. In our assays we use crotonyl-CoA as the substrate of FabI where coenzyme A is substituted for ACP.