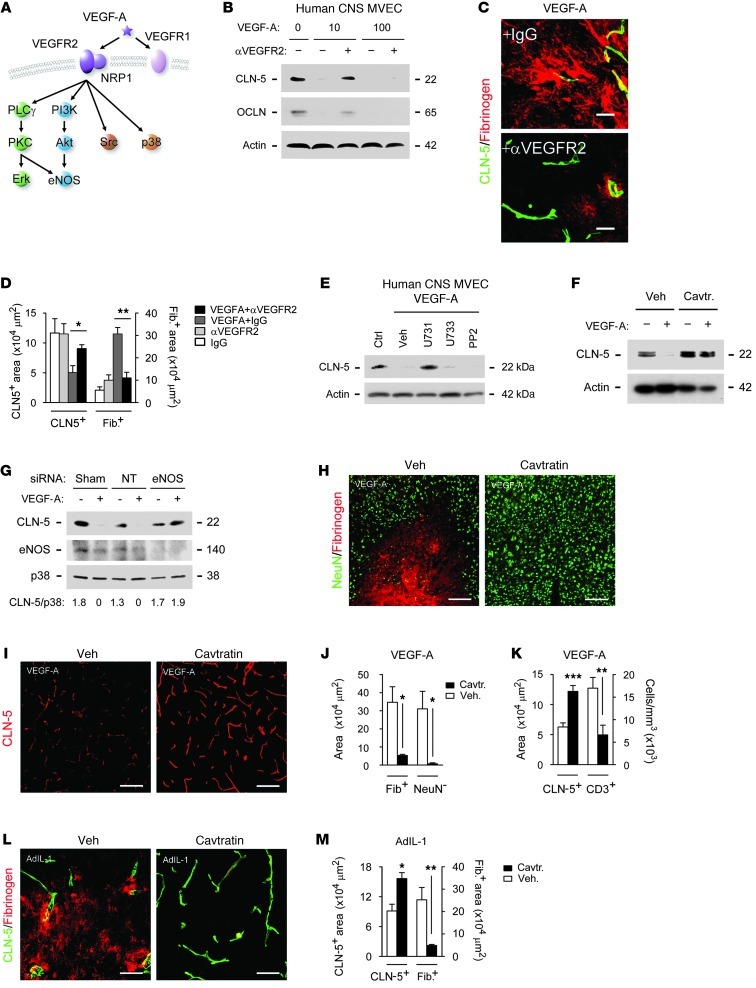
Figure 7. Effects of VEGF-A on CLN-5 are mediated via eNOS.
(A) VEGF-A signaling pathways. (B) Human CNS MVECs were pretreated with 10 ng/ml anti-VEGFR2 or IgG for 2 hours, then VEGF-A or vehicle for 24 hours, and CLN-5 and OCLN levels were determined by immunoblot. (C and D) 12-week-old C57BL/6 mice (3 per group) received cortical coinjection of 20 ng VEGF-A or vehicle, plus 2 μg anti-VEGFR2 or IgG, and were sacrificed at 24 hours for determination of CLN-5 and fibrinogen area. (E and F) Immunoblot for CLN-5 in VEGF-A–treated human CNS MVECs also (E) treated with 5 μM U73122, 10 ng/ml VEGF-A, 5 μM U73343, or 3 μM PP2 or (F) pretreated with 2 μM cavtratin. (G) Immunoblot for CLN-5, eNOS, and p38 (representative of other signaling components) in human MVECs nucleofected with sham, nontargeting (NT), or eNOS siRNA. CLN-5/p38 ratio is shown below. (H–M) 12-week-old C57BL/6 mice (3 per group) received 2.5 mg/kg cavtratin or vehicle i.p., then 30 minutes later received cortical injection of (H–K) 60 ng VEGF-A, followed by sacrifice at 24 hours, or (L and M) 107 pfu AdIL-1, followed by daily cavtratin until sacrifice at 7 dpi. Immunostaining and morphometry for NeuN, fibrinogen, CLN-5, and CD3 are shown. Scale bars: 20 μm (C); 150 μm (H, I, and L). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ANOVA plus Bonferroni test (D) or Student’s t test (J, K, and M). Results are representative of at least 3 separate cultures (B and E–G) or 3 independent experiments (C, D, and H–M).