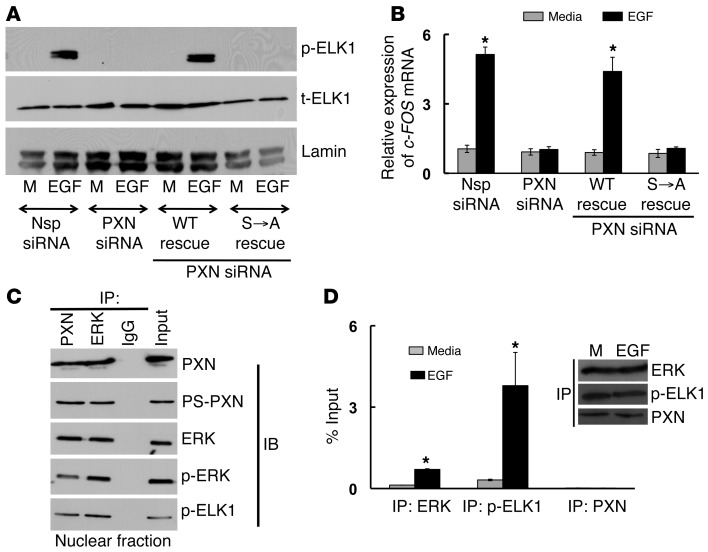
Figure 6. PS-PXN regulates c-FOS mRNA expression in the nucleus by complexing with ERK and ELK1 to allow ERK-mediated activation of ELK1.
(A and B) PS-PXN is essential for EGF-induced phosphorylation of ELK1 and c-FOS mRNA expression. Immunoblot (A) and qPCR (B) analysis in PC3 cells (treated with Nsp or PXN-specific siRNA) showing EGF-induced (20 ng/ml; 30 minutes) (A) phosphorylation of ELK1 and (B) c-FOS mRNA expression. PXN-knockdown cells were also transfected with plasmids expressing WT PXN or PXN lacking the MAPK-targeted serines (S→A). Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.005 relative to medium. (C) PS-PXN forms a complex with ERK and ELK1 in the nucleus. IP assays were performed in nuclear extracts of LNCaP cells treated with EGF (20 ng/ml, 24 hours) (n = 3 experiments with identical results). Either PXN, PS-PXN, ERK, p-ERK, or p-ELK1 were precipitated, followed by immunoblotting as indicated. (D) ERK and ELK1, but not PXN, bind to the c-FOS promoter in EGF-stimulated PC3 cells. PC3 cells were serum starved overnight, followed by treatment with medium or EGF (20 ng/ml) for 24 hours, before chromatin IP. The occupancy of ERK, p-ELK1, and PXN on c-FOS promoter was examined. Values are presented as percentage input (mean ± SEM, n = 3). *P ≤ 0.005 with respect to medium. Representative immunoblot shows equal amounts of ERK, p-ELK1, and PXN were IP from medium (M) and EGF-treated samples.