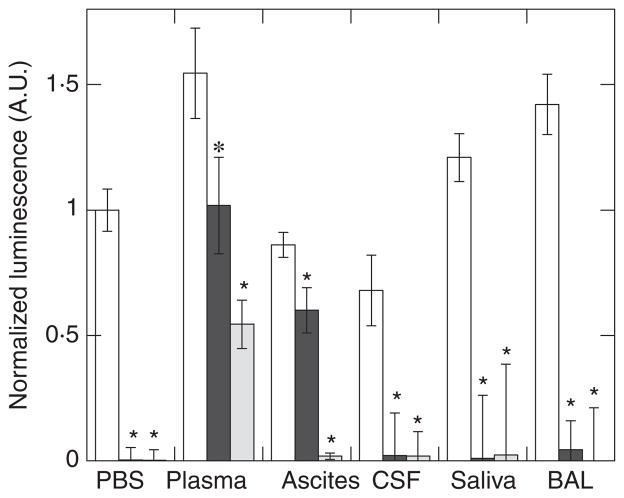
Figure 3.
Antibacterial activity of CSA-13 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Xen 5 in human body fluids was determined by luminescence readings 6 h after addition of equal amounts of bacteria to an equal volume of phosphate buffered saline (PBS), or PBS supplemented with 50% of plasma, ascites, cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF), saliva or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). In each condition, the white column indicates luminescence signal in control samples. Black and grey columns indicate luminescence signal in the presence of 10 and 30 μmol l−1 CSA-13 respectively. Data from one experiment performed in triplicate are shown. Two other experiments with samples obtained from different subjects show similar trends. *Significantly different from control sample.