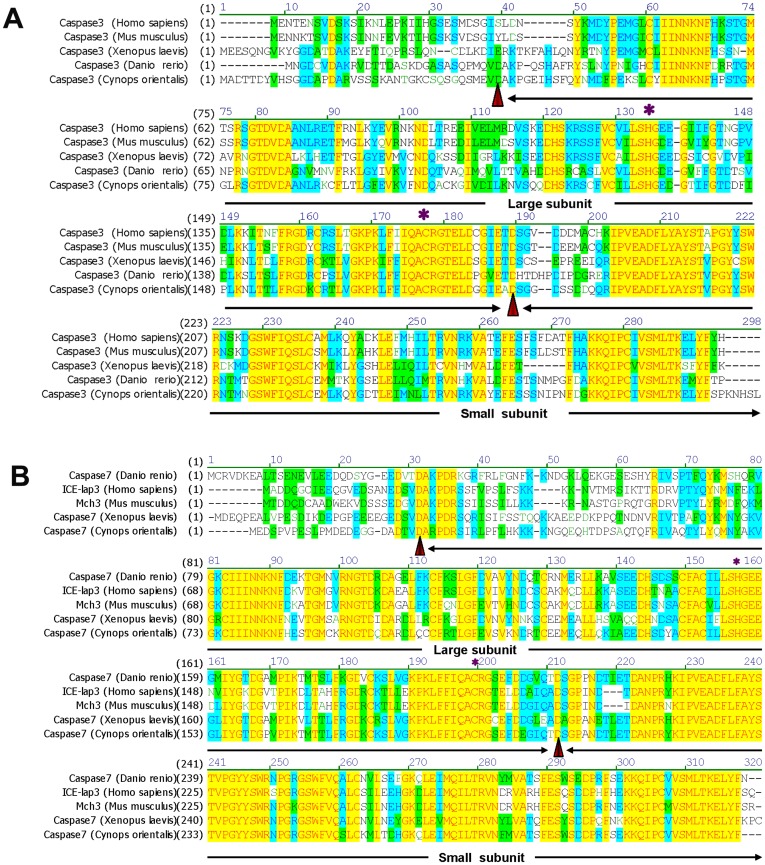
Figure 5. Multiple alignments of Caspase3 and Caspase7 in Cynops orientalis with their homolog from several vertebrates.
The protein alignment was performed using Vector NTI10 (Invitrogen) with the following sequences: (A) Cynops orientalis(JQ320088); Danio rerio(CAX14649.1); Xenopus laevis (NP_001081225.1); Homo sapiens (P42574); Mus musculus (P70677); (B) Cynops orientalis (JQ320087); Homo sapiens (AAC50346.1); Mus musculus(BAA19730.1); Xenopus laevis (NP_001091272.1); Danio rerio (AAH95327.1). The identities of Caspase3 in Cynops orientalis with its homolog were 56.2% (Danio rerio), 54.4% (Xenopus laevis), 57.6%(Homo sapiens) and 56.3% (Mus musculus). The identities of Caspase7 in Cynops orientalis with its homolog were 67.6% (Danio rerio), 64.6% (Xenopus laevis), 62.6% (Homo sapiens) and 62.3% (Mus musculus). Putative cleavage sites at aspartic acid residues, which separate Caspase3 and Caspase7 into large subunits and small subunits, are labeled red arrowheads. Histines and Cystines that are essential for the catalytic centre of Caspase3 and Caspase7 are indicated by asterisk.