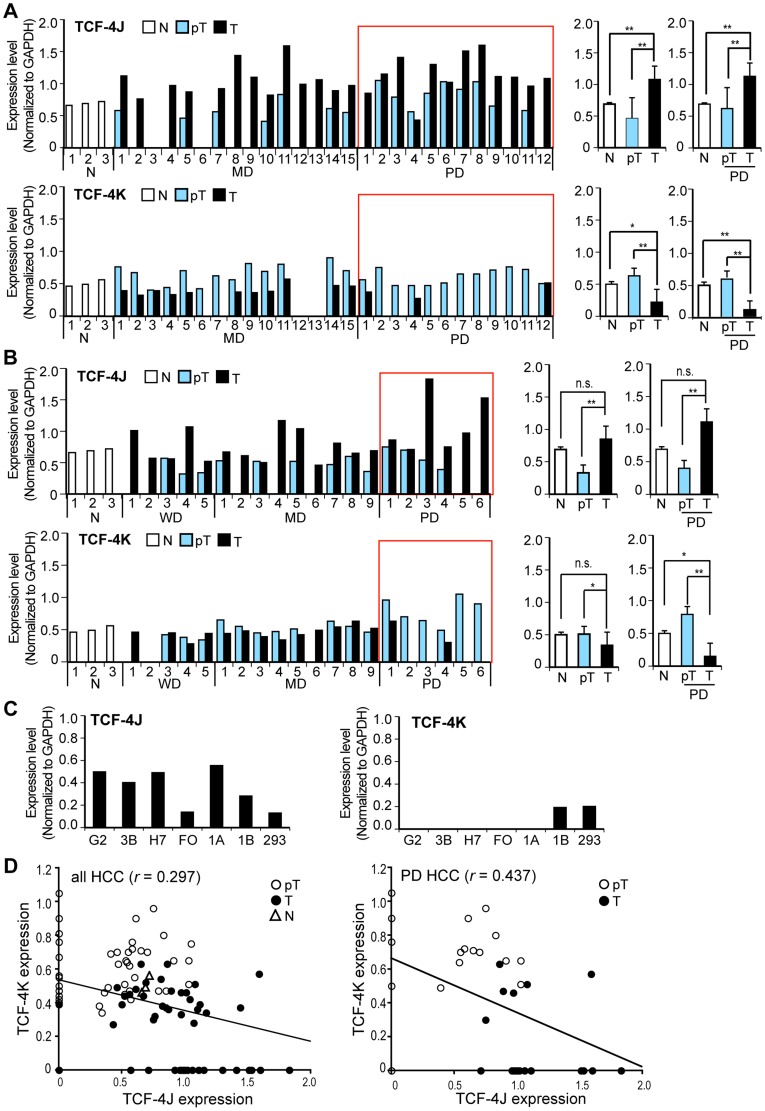
Figure 1. Expression of TCF-4J and TCF-4K mRNAs was different in human HCCs.
(A) Comparative analysis of TCF-4J and K mRNA expression levels in 27 HBV-related HCC tumors (T) adjacent peritumor tissue (pT) and histologic normal liver (N) by RT-PCR. Values are normalized to GAPDH. Red rectangles denote poorly differentiated (PD) HCC. WD, well differentiated; MD, moderately differentiated. Statistical results from all tissues or PD HCC are expressed as mean + SD (right panel). (B) Another 20 HCC tumors including five WD HCCs from a different clinical site. Seventeen individuals had HCV-related chronic liver disease, and the remainder had chronic HBV infection. See also Tables 1 and 2. (C) Expression levels of TCF-4J and K mRNA in human cell lines HepG2 (G2), Hep3B (3B), Huh-7 (H7), FOCUS (FO), HAK-1A (1A), HAK-1B (1B), OUMS-29 (OU), and HEK293 (293). (D) Inverse correlation between TCF-4J and K expression in all HCC (left panel) and PD HCC (right panel). Note the weak inverse correlation in all cases (r = 0.297), while increased inverse correlation in PD HCC (r = 0.437). *p<0.01; **p<0.05.