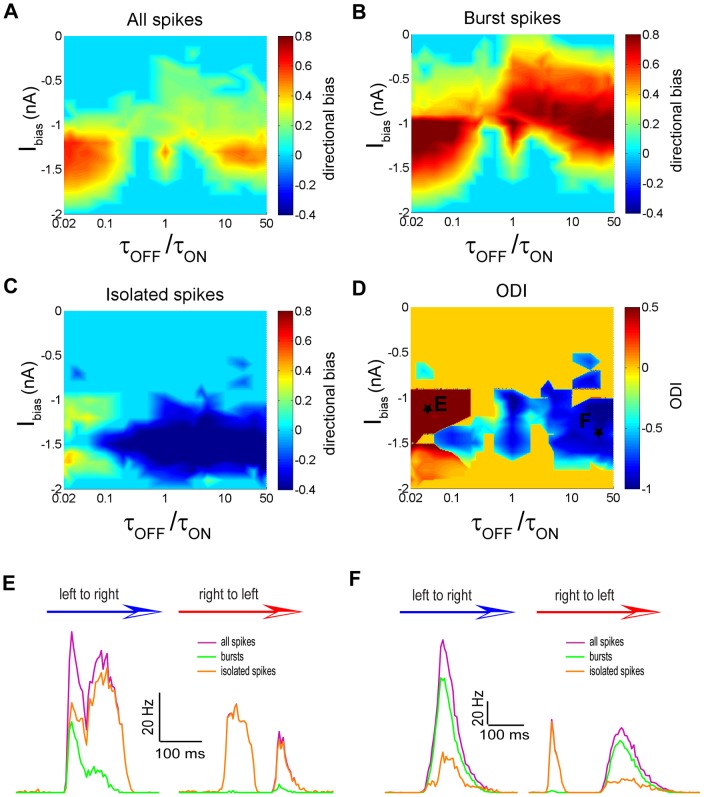
Figure 6. The bias current Ibias and synaptic depression time constant ratio τOFF/τON strongly influence movement direction coding by bursts and isolated spikes.
A) Directional bias computed from the full spike train as a function of τOFF/τON and Ibias. B) Directional bias computed from the burst train as a function of τOFF/τON and Ibias. C) Directional bias computed from the isolated spike train as a function of τOFF/τON and Ibias. D) Opposite direction selectivity index as a function of τOFF/τON and Ibias. E) PSTH values near the maximum values in the left to right (blue arrow) and right to left (red arrow) directions for the full spike (purple), burst (green), and isolated (orange) spike trains for an example data point marked with a star in panel D. F) PSTH values near the maximum values in the left to right (blue arrow) and right to left (red arrow) directions for the full spike (purple), burst (green), and isolated (orange) spike trains for another example data point marked with a star in panel D.