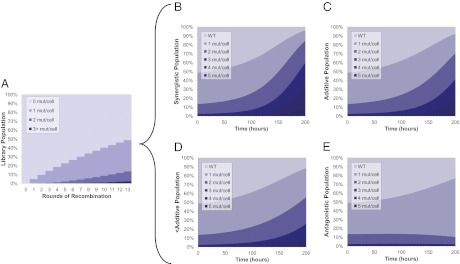
Fig. 3.
Model of recursive multiplex recombineering library growth. (A) Construction of the library. Recombination efficiencies of 2–10% were routinely achieved, as quantified using an oligo that restores operational sequence of the galK gene in the SIMD70 strain (oligo 478 in ref. 19). Shown is the theoretical population distribution of the library where recombination efficiency is 5.0%. After 13 rounds of recombination, single, double, and triple mutants represent 35%, 11%, and 2%, of the total library populations, respectively. (B–E) Four cases of varying epistasis in a growth selection. WT growth rate was set to 0.05 1/h (typical for 40% hydrolysate growth). Mutations were modeled to be either beneficial (35% increase in growth rate over control; 10% of mutations) or neutral (no change in growth rate; 90% of mutations). (B) Synergistic: combinations of mutations increase in growth 10% more than additive. (C) Additive: benefits of individual mutations are additive. (D) Less-than-additive: combinations 10% less than additive. (E) Antagonistic: combinations of mutations reduce growth rate by 15% compared with individual mutations.