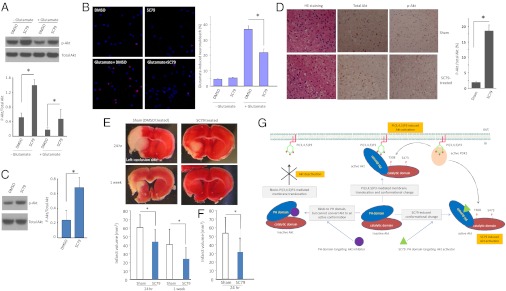
Fig. 4.
SC79 suppresses excitotoxicity and alleviates stroke-induced neuronal death. (A) SC79 elevated Akt activation in cultured cortical neurons. All samples were normalized to the amount of total Akt. Data presented are the means (±SD) of three independent experiments. (B) SC79 suppresses excitotoxicity-induced neuronal death. Primary neuronal cultures (14 d) were treated with 50 μM glutamate for 40 min, and toxicity was assayed 4 h after glutamate exposure. Cell viability was assessed by fluorescence microscopy after Hoechst nuclear staining and propidium iodide (PI) staining. At least three separate experiments were performed with a minimum of 1,000 neurons counted per data point. The results are the means of three independent experiments. Bars indicate means ± SD. (C) SC79 treatment led to Akt hyperactivation in the brain of live animals. Protein extracts collected from the brain of untreated and SC79-treated mice were resolved on SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. SC79 was applied via i.p. injection at a concentration of 0.04 mg/g of body weight. Data are from five independent experiments (mean ± SD). *P < 0.05 (Student t test). (D) SC79 enhanced Akt activity during neuronal cell death in an in vivo mouse ischemia model. Mice (C57 Black/6) were subjected to permanent focal cerebral ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 24 h. Brain slices around ischemic penumbra were prepared, and total and phosphorylated Akt/PKB were analyzed. Data are representative of five experiments. (E) SC79 alleviated stroke-induced neuronal death. Infarct volume was assessed in SC79 treated and Sham-treated control mice at each indicated time points. Data are from five independent experiments (mean ± SD). *P < 0.05 (Student t test). SC79 was injected i.p. once (0.04 mg/g of mouse body weight) 5 min before permanent MCAO. (F) The experiment was conducted as described above except that extra SC79 was injected (0.04 mg/g of mouse body weight, once per hour for 6 h). (G) Schematic model of SC79-induced Akt hyperactivation.