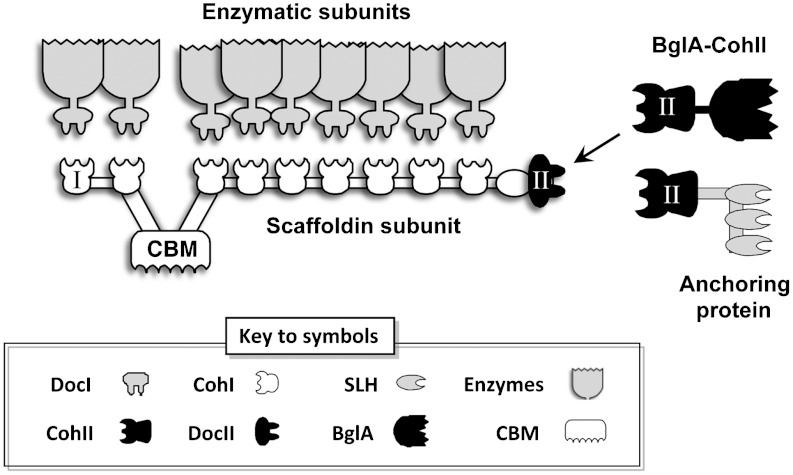
Fig. 1.
Schematic view of the C. thermocellum cellulosome and the proposed attachment of the chimeric β-glucosidase-fused type-II cohesin (BglA-CohII). The type-I cohesin-dockerin interaction integrates the dockerin-containing enzymatic subunits into the complex via interaction with the scaffoldin-borne type-I cohesins, whereas the carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) binds the complex to the insoluble substrate. C. thermocellum can produce over 70 different dockerin-bearing enzymes that are integrated into the cellulosome through interaction with any of the nine cohesins of the scaffoldin subunit. In the cell surface-attached state, the cellulosomal DocII module binds selectively to the CohII of an anchoring protein. In the cell-free state, unoccupied DocII positions can be used for specific incorporation of BglA-CohII into the purified cellulosome.