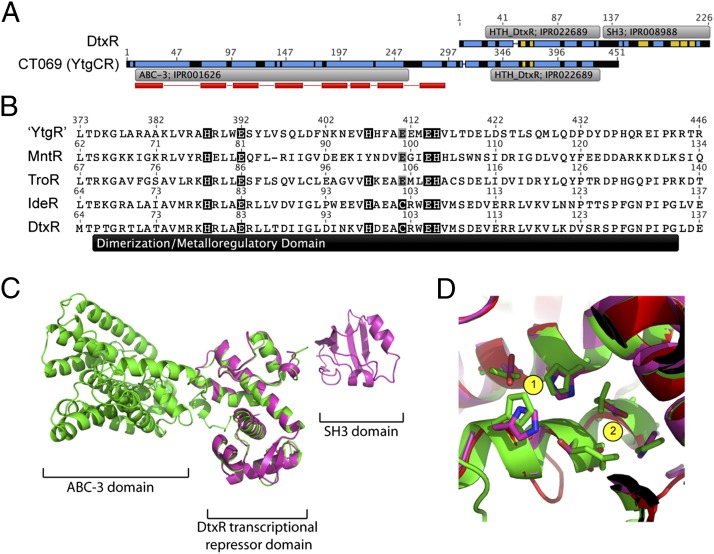
Fig. 1.
Bioinformatics analysis indicates that the ct069 (ytgCR) locus encodes a permease-repressor fusion protein. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment shows that CT069 (YtgCR) exhibits homology to DtxR in the C terminus. Recognized InterPro domains (EBI InterPro database) are annotated. Predicted membrane spanning regions are indicated by red bars below YtgCR sequence (TMHMM); the most probable arrangements of topology result in the C terminus of YtgCR localizing to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Secondary structures (predicted by Phyre or previously resolved) are indicated by blue (α-helix) and yellow (β-sheet). (B) Sequence alignment of the dimerization/metalloregulatory domain for the “YtgR” domain within Ct069 [C. trachomatis, MntR (B. subtilis), TroR (T. pallidum), IdeR (M. tuberculosis] and DtxR (C. diphtheriae). Residues involved in metal coordination in the DtxR holoenzyme (23) that are conserved are highlighted in black. Putative conservative substitutions are highlighted in gray. (C) Overlay of Phyre2 server modeled YtgCR (green) and DtxR (magenta) (PDB - 1g3w). (D) The divalent metal-binding sites of DtxR (magenta) are conserved in the YtgR domain (green). Site 1 residues are identical in both proteins, whereas Cys102 is replaced by Glu in the YtgR domain.