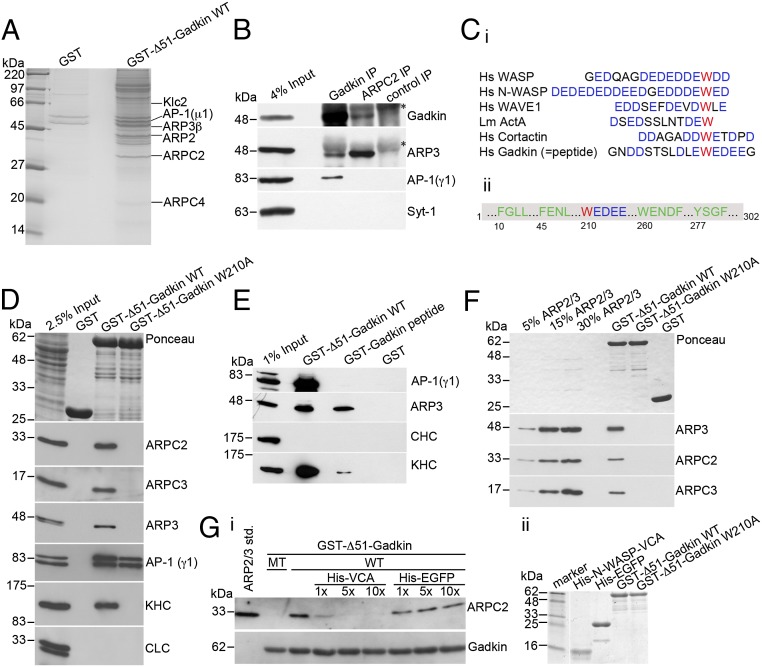
Fig. 2.
Gadkin directly interacts with ARP2/3 via a tryptophan-containing acidic cluster motif. (A) Coomassie blue-stained gel of material isolated by affinity chromatography from 12.5 mg of rat brain extract using 1.5 mg of GST or GST-fused Δ51-Gadkin cross-linked to glutathione Sepharose beads as bait. The labeled bands were identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. (B) Endogenous ARP2/3 and Gadkin coimmunoprecipitate. Solubilized rat brain membranes were subjected to immunoprecipitation using affinity-purified antibodies against Gadkin, ARPC2, or nonspecific rabbit IgGs as control. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for Gadkin, ARP3, AP-1, and synaptotagmin 1 (Syt-1). Asterisks denote nonspecific bands originating from Ig-heavy chains. (Ci) Sequence alignment of ARP2/3-interacting A domains of classic NPFs and Gadkin. Acidic residues are shown in blue, and the critical W is in red. (Cii) Scheme of Gadkin primary structure highlighting amino acid positions of motifs involved in binding to AP-1 (green) or ARP2/3 (red/blue). (D) Immunoblot analysis of proteins isolated by affinity chromatography from 1.6 mg of rat brain extract using 20 μg of GST-tagged Δ51-Gadkin-WT or its W210A mutant as bait. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for ARPC2, ARPC3, ARP3, AP-1, kinesin heavy chain (KHC), and clathrin light chain (CLC). (E) Immunoblot analysis of material affinity-purified using GST, GST-Δ51-Gadkin, or a GST-Gadkin-peptide as described in C as baits. (F) Direct binding of purified ARP2/3 complex to GST-Δ51-Gadkin. No binding is seen for Gadkin-W210A or GST. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for ARP3, ARPC2, and ARPC3. (Gi) Binding of purified ARP2/3 to GST-Δ51-Gadkin is inhibited by addition of a 1–10× molar excess of His6-N-WASP-VCA domain. Addition of His6-EGFP as a control did not affect binding. Samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for ARPC2 and Gadkin. (Gii) Integrity of purified proteins was verified by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie staining.