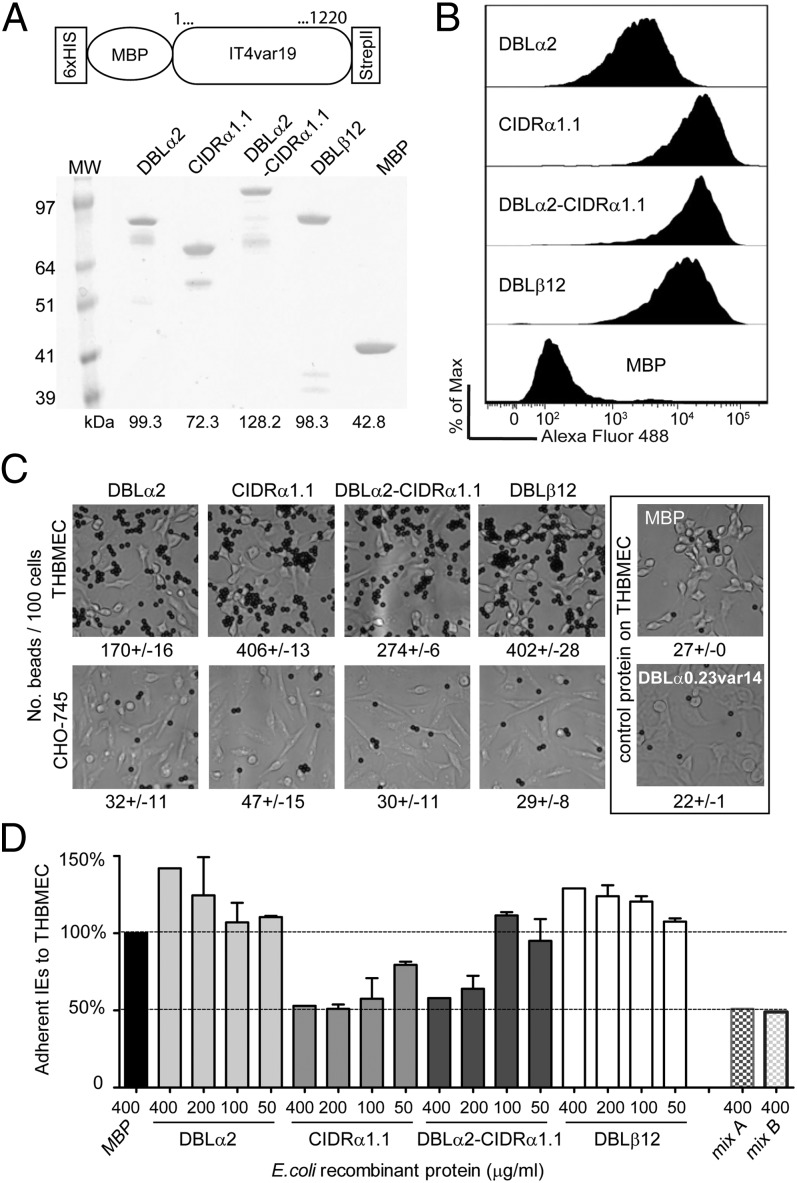
Fig. 6.
DC8-var19–encoded recombinant proteins exhibit binding capacity for brain endothelium. (A) Schematic of the protein construct. Protein boundaries are the following: DBLα2, M1-V484; CIDRα1.1, C485-C732; DBLα2-CIDRα1.1, M1-C732; and DBLβ12, P733-C1220. Proteins were analyzed on SDS/PAGE gel and visualized with GelBlue code. (B) Recombinant proteins binding to unfixed THBMEC cells were determined by flow cytometry. Recognition via the anti-strepII tag antibody tag is shown. (C) Protein-coupled Dynal Bead binding assays to THBMEC cells or CHO-745 cells as a negative control. Results are expressed as mean of beads binding per 100 cells ± SDs. (D) Binding of the IT4var19-expressing parasite clone (1E2) to transformed HBMECs in the presence of each of the E. coli fusion recombinant proteins, from 0.4 mg/mL to 0.05 mg/mL final concentration. Mix A corresponds to 0.4 mg/mL of three single domains DBLα2, CIDRα1.1, and DBLβ12 combined and mix B to 0.4 mg/mL of the tandem domain plus the DBLβ12 domain combined. The percentage of binding is expressed relative to binding in the presence of control protein MBP. Results are expressed as mean ± SDs from two independent experiments.