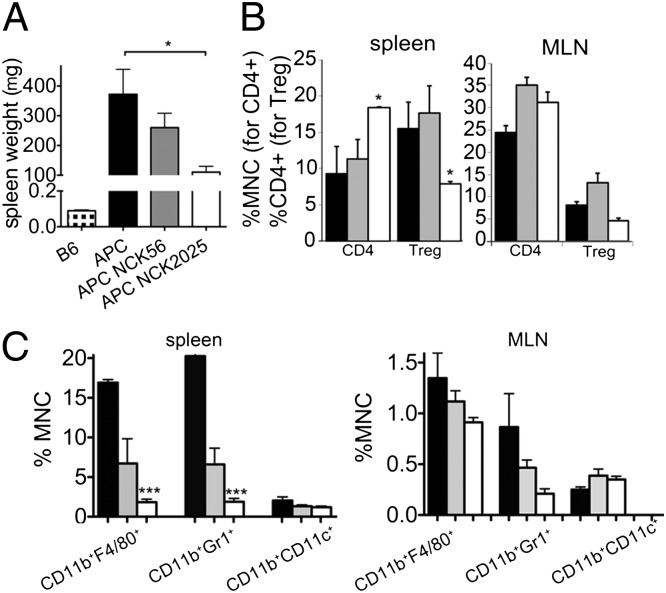
Fig. 5.
Attenuation of systemic inflammation in TS4Cre × cAPClox468 mice by NCK2025 treatment. (A) Splenic weights in TS4Cre × cAPClox468 mice (n = 5 per group) that were untreated or treated with L. acidophilus strains (*P < 0.026). (B) Frequencies of CD4+Foxp3− effector T cells and CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs in the spleen and MLN of untreated and treated TS4Cre × cAPClox468 mice; splenic CD4+ T cells (*P < 0.065) and splenic Tregs (P < 0.026). (C) Frequencies of CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages, CD11b+Gr1+ granulocytes, and CD11b+CD11c+ DCs among spleen-derived leukocytes of untreated or treated mice; splenic CD11b+F4/80+ cells (***P < 0.0001) and splenic CD11b+Gr1+ cells (***P < 0.0004). (C) Same frequencies among MLN-derived leukocytes. Histograms show compiled results with SEM; trends shown were not statistically significant. Student t test was performed with two tails, type 2 between untreated and treated groups. Single cell suspensions were filtered (40 μm), and red blood cells were lysed by using Ack Lysing Buffer (BioWhittaker). Cells were washed and then incubated with Fc block (BD Bioscience). Dead cells were excluded (LIVE/DEAD Violet Dead cell Stain kit; Invitrogen). Antibodies used were CD11c FITC (HL3), GR1 APC (RB6-8C5), CD4 Percp (RM4-5), CD25 biotin (7D4), and streptavidin FITC (BD Pharmingen); and F4/80 Percp (BM8) and CD11b PE-Cy7 (M1/70; Biolegend). Data were acquired with a FACSCanto II device (BD) and analyzed by using FlowJo software (Tree Star). Black bars indicate untreated mice, gray bars NCK56-treated mice, and white bars NCK2025-treated mice. Data are representative of two independent experiments.